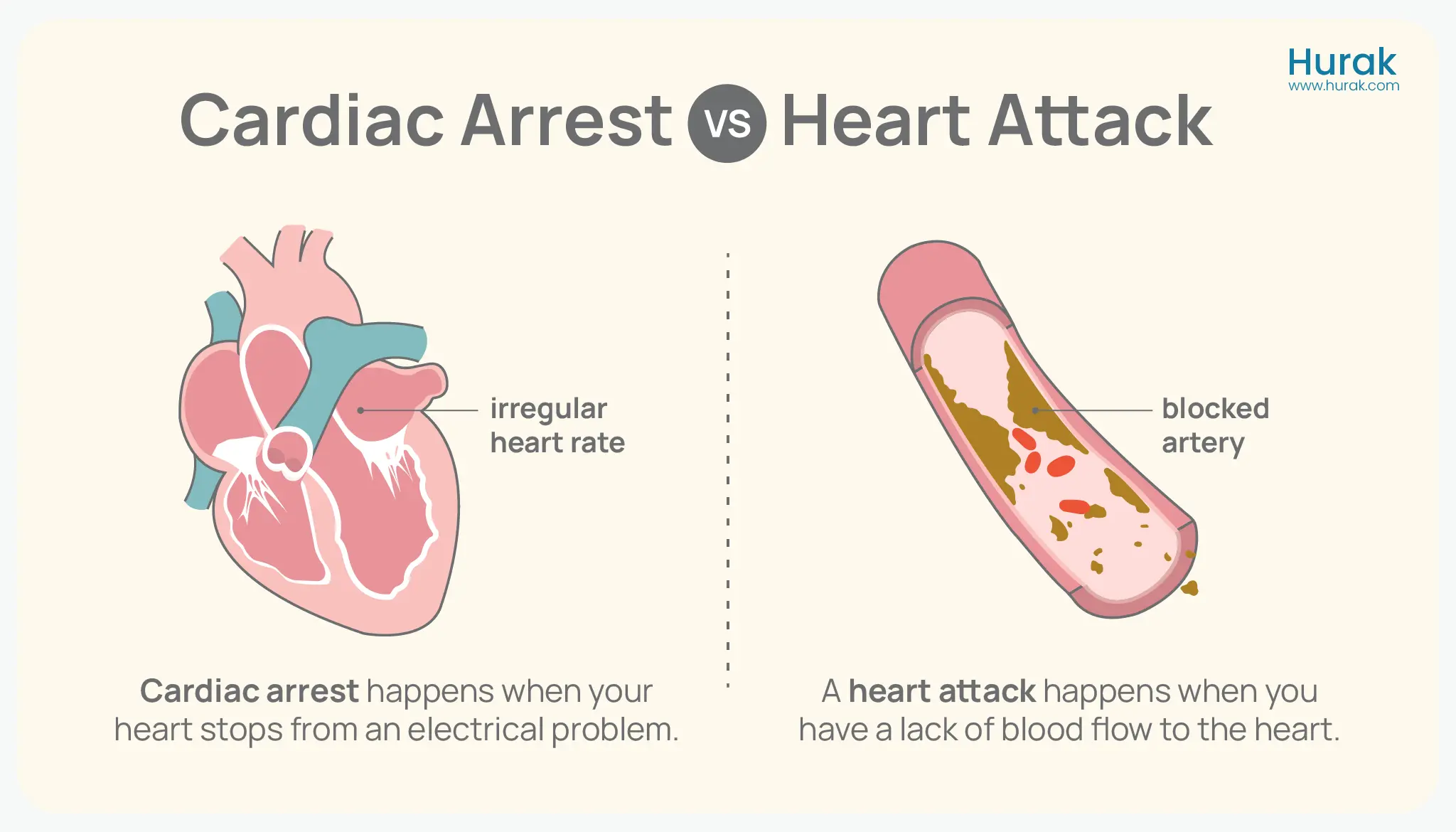
Heart attack and cardiac arrest might sound similar, but they are different heart conditions. Both are serious and life-threatening, but their causes and treatments differ.
A heart attack is a “plumbing problem” caused by a blockage in the arteries. Cardiac arrest is an “electrical problem” caused by the heart’s rhythm malfunctioning.
What is a Cardiac Arrest?
Cardiac arrest happens when the heart suddenly stops beating. This stops blood flow to the brain and other vital organs, leading to unconsciousness and, if untreated, death within minutes.
Cardiac arrest is often caused by an electrical problem in the heart, like an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia). It can happen suddenly without warning, even in someone who seems healthy.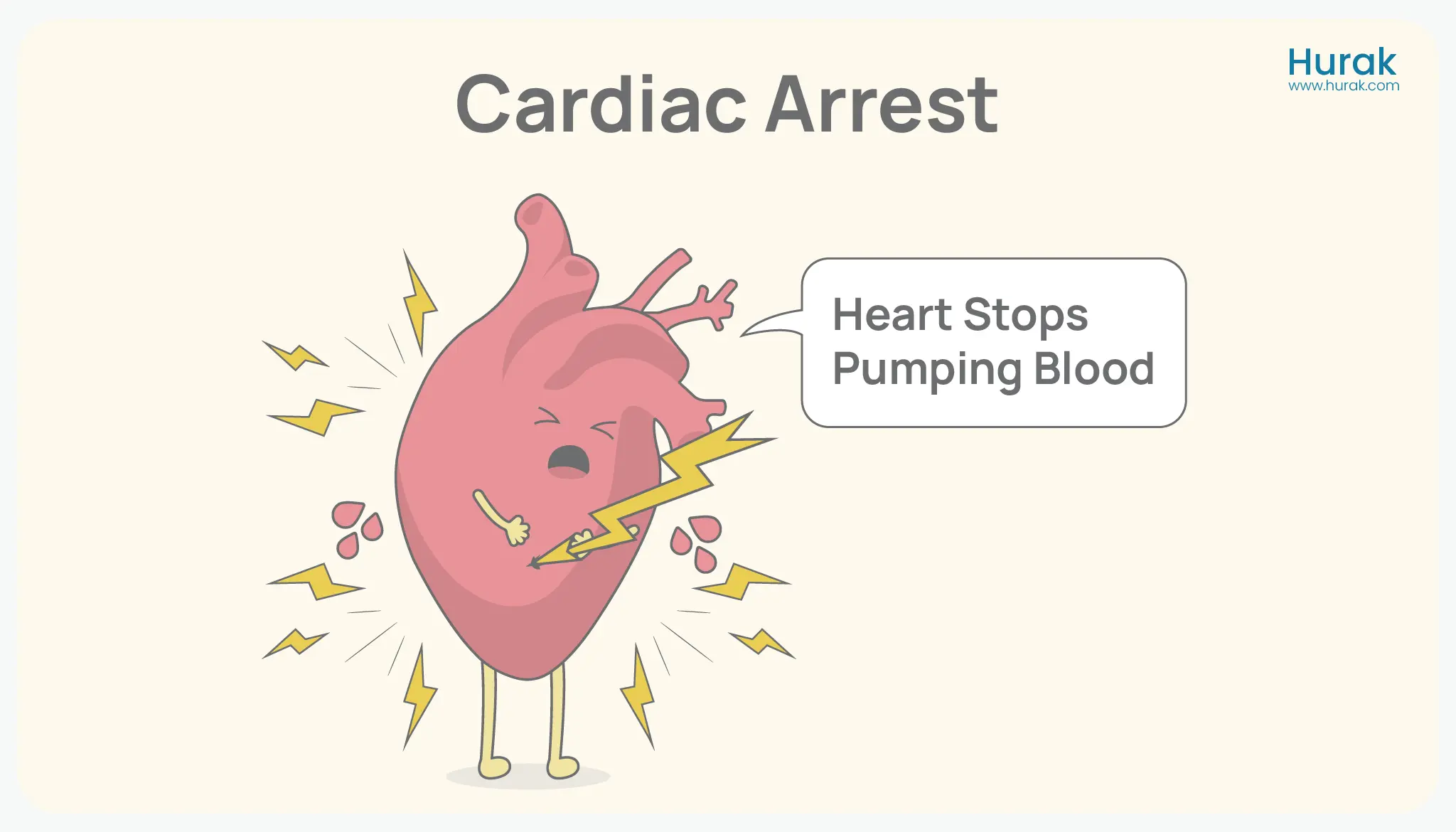
What is a Heart Attack?
A heart attack, also called a myocardial infarction (MI), occurs when blood flow to a part of the heart is blocked. This blockage is usually caused by a buildup of fat, cholesterol, or plaque in the arteries.
During a heart attack, the affected part of the heart doesn’t get enough oxygen, which can damage the heart muscle. Unlike cardiac arrest, the heart usually continues to beat during a heart attack.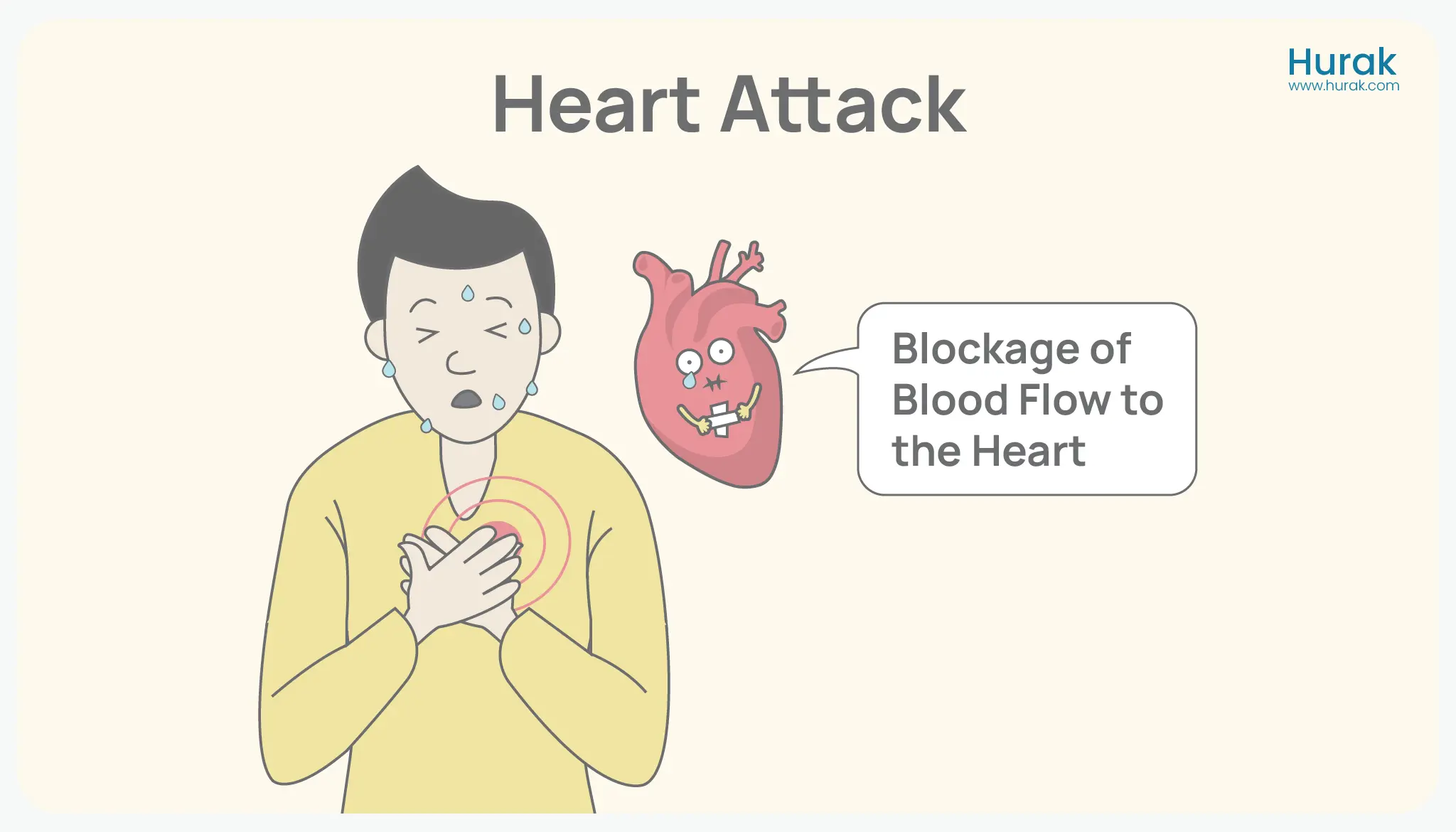
Is Cardiac Arrest a Heart Attack?
No, cardiac arrest is not the same as a heart attack. However, a heart attack can sometimes lead to cardiac arrest. In this case, the damage caused by the heart attack triggers the heart to stop beating.
What is the Difference Between Heart Attack and Cardiac Arrest?
The main difference is what causes each condition and how it affects the heart. A heart attack, also known as a myocardial infarction (MI), occurs when a blockage prevents oxygen-rich blood from reaching the heart. Cardiac arrest, on the other hand, happens when the heart suddenly stops working. In this case, the heart stops beating and pumping blood to vital organs.
Although one results from a blockage and the other from an electrical malfunction in the heart, you can reduce the risk of both. Focus on improving your overall heart health by maintaining a healthy weight, managing blood pressure, and keeping cholesterol levels in check.
Heart Attack Vs Cardiac Arrest | ||
Feature | Heart Attack | Cardiac Arrest |
Cause | Blockage in blood flow to the heart | Electrical malfunction in the heart |
Symptoms | Chest pain, shortness of breath, nausea | Sudden collapse, no pulse, no breathing |
Heart Function | The heart keeps beating, though damaged | The heart stops beating completely |
Onset | Gradual, with warning signs | Sudden, often without warning |
Treatment | Emergency medication, surgery (like stents) | CPR, and defibrillation (AED) are needed immediately |
How to Reduce Your Risk of Heart Attack and Cardiac Arrest
To lower your chances of experiencing either a heart attack or cardiac arrest:
- Eat a heart-healthy diet with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Exercise regularly to maintain a healthy weight.
- Monitor your blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
- Avoid smoking and limit alcohol consumption.
Understanding the difference between heart attack and cardiac arrest can save lives. Knowing the symptoms and getting immediate help is the key to better outcomes.
FAQs
Can a heart attack lead to cardiac arrest?
Yes, a severe heart attack can sometimes cause cardiac arrest. The damage from a heart attack can disrupt the heart’s electrical system, leading to sudden cardiac arrest.
What should I do if I see someone experiencing cardiac arrest?
Call emergency services immediately. Start CPR (chest compressions) and use an automated external defibrillator (AED) if one is available. Quick action can save a life.
How can I tell the difference between a heart attack and cardiac arrest?
A heart attack usually involves symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, and nausea, and the person is often awake. Cardiac arrest happens suddenly, causing the person to collapse, lose consciousness, and stop breathing.
Are heart attacks and cardiac arrests preventable?
While the risk cannot be eliminated, it can be significantly reduced by maintaining a healthy lifestyle, managing blood pressure and cholesterol, and avoiding smoking.
Who is at higher risk of cardiac arrest?
People with a history of heart disease, arrhythmias, or previous heart attacks are at higher risk. However, cardiac arrest can also occur in people without any known heart problems.
Which is more dangerous, heart attack or cardiac arrest?
Cardiac arrest is more dangerous than a heart attack as it stops the heart completely, risking immediate death without prompt treatment.

How To Administer CPR ?
Knowing the difference between cardiac arrest and heart attack is important in emergencies, but there's more to first aid. Our First Aid courses offer complete training to help you handle critical situations. Whether you want to improve your skills or workplace safety, these courses help build confidence and expertise. View our Emergency First Aid at Work (EFAW) and Level 3 First Aid at Work courses. These courses meet the UK legal requirements and help you keep people safe.
Conclusion
Understanding the difference between heart attack and cardiac arrest is important for recognising and responding to these emergencies. A heart attack involves a blockage in blood flow, while cardiac arrest is a sudden stoppage of the heart’s function. Both conditions require immediate medical attention.
By learning the symptoms, knowing how to act in emergencies, and improving your heart health, you can help save lives and reduce risk. Remember, awareness is the first step toward prevention and better heart health.