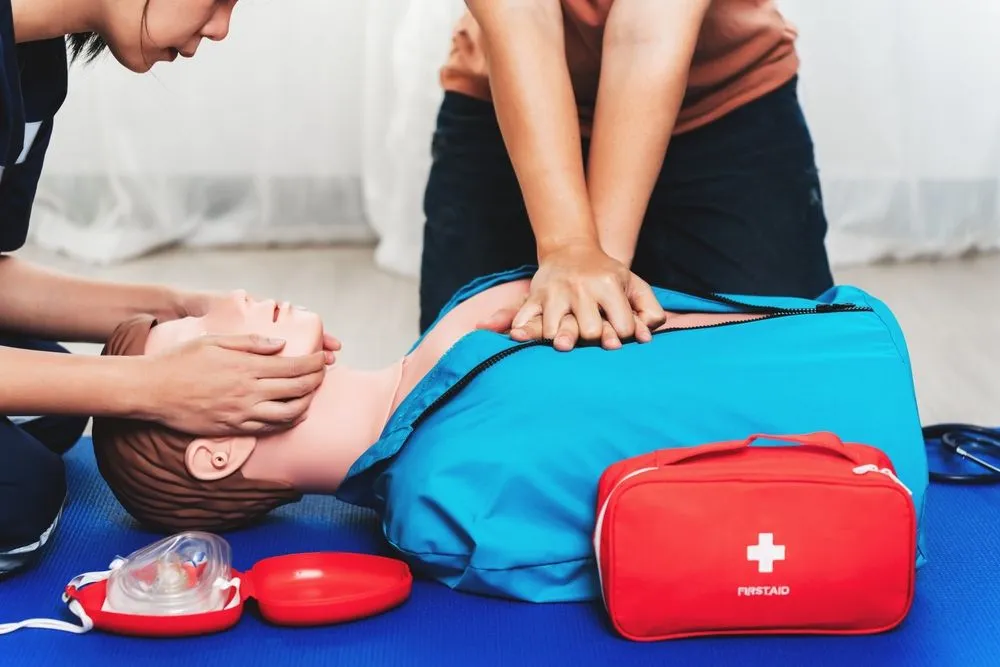
A cardiac arrest is a sudden and often fatal condition in which the heart stops pumping blood, leading to a loss of circulation. This requires serious medical attention. It is imperative that we understand the signs of cardiac arrest, what the causes might be, and the immediate first aid actions that can help save a life.
What Causes Cardiac Arrest?
The primary cause of cardiac arrest is a malfunction in the heart’s electrical system, which disrupts the heart’s rhythm and its pumping ability.
Common causes include:
- Arrhythmias: Abnormal heart rhythms, such as ventricular fibrillation.
- Heart Disease: Conditions like coronary artery disease or previous heart attacks.
- Electrolyte Imbalances: Either extremely high or low levels of certain minerals like potassium and magnesium that are associated with the functionality of the organs.
- Trauma or Severe Bleeding: Can disrupt the heart’s function.
- Genetic Disorders: Conditions like Long QT Syndrome or cardiomyopathies.
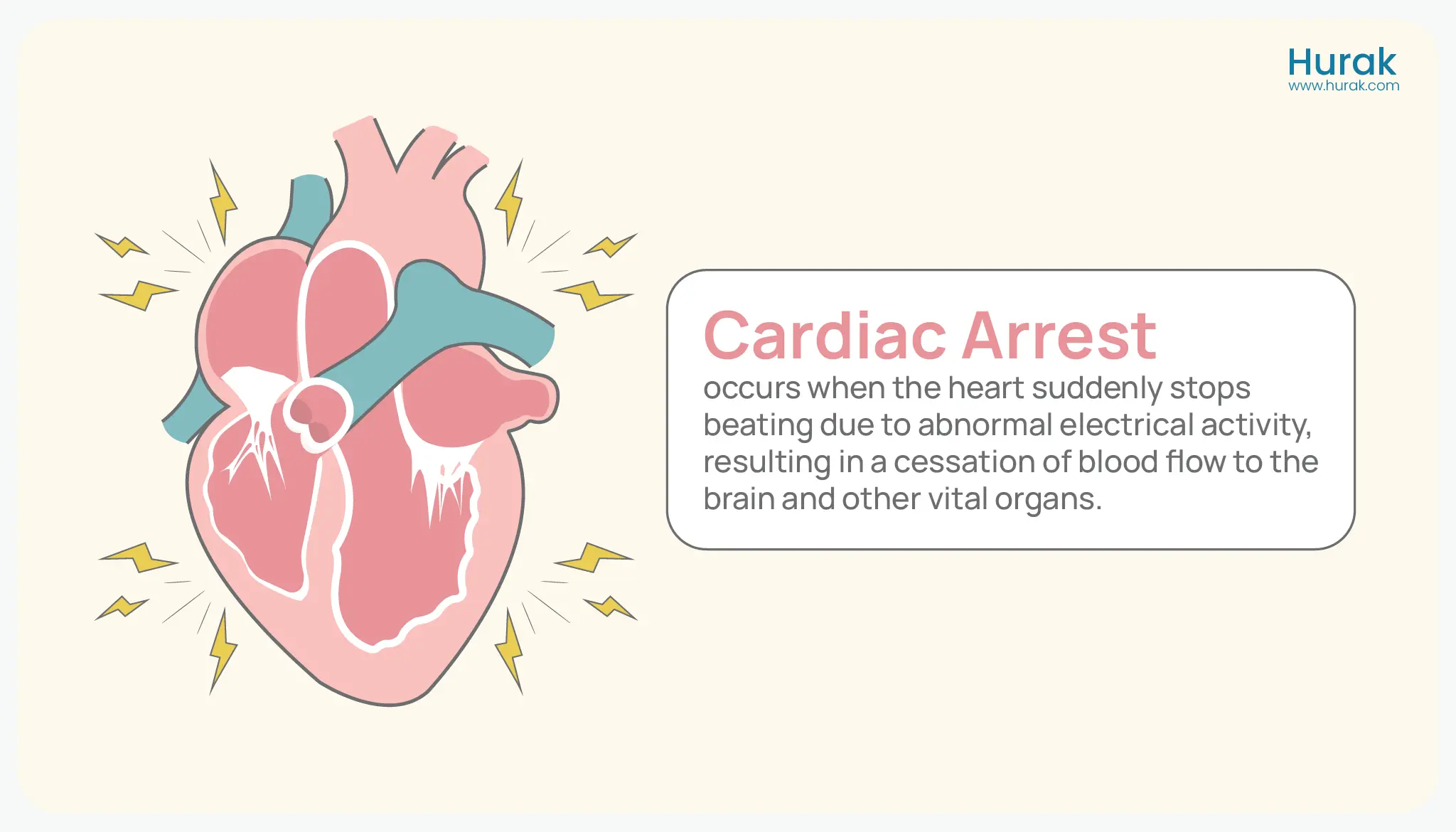
Is Cardiac Arrest a Heart Attack?
Even though the two are related there is a stark difference between a cardiac arrest and a heart attack. A heart attack is the result of blockage of blood flow to the heart, causing severe damage. Whereas the latter results from an electrical malfunction in the heart, leading to the heart to stop its pumping action.
Signs of Cardiac Arrest and Cardiorespiratory Arrest
Being able to recognize the signs of a cardiac arrest is crucial, below you will find a list of signs that will help you recognize the signs so that you can act quickly and get the person the help they need.
- Collapsing suddenly
- When there is no pulse and the person isn’t breathing
- If the person loses consciousness
Some cases may present early signs and symptoms, these include:
- Chest pain or discomfort
- Shortness of breath
- Palpitations or feeling dizzy
When the heart and lungs fail simultaneously, it is called cardiorespiratory arrest, which presents similar symptoms.
Cardiac Arrest First Aid
Acting swiftly without wasting a second is crucial in responding to cardiac arrest. Follow these steps for effective first aid:
- Call Emergency Services: Dial your local emergency number immediately.
- Start CPR: As soon as the person collapses, start performing chest compressions at a rate of 100-120 per minute to ensure that blood flows to vital organs.
- Use a Defibrillator: If it’s within your reach immediately use a defibrillator to restore the heart’s rhythm.When using the device make sure you are following the voice commands accurately.
Preventing Cardiac Arrest
While not all cases can be prevented, you can lower the risk by:
- Managing chronic health conditions like high blood pressure and diabetes.
- Avoiding smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
- Maintaining a healthy diet and exercising regularly.
- Getting regular check-ups, especially if you have a family history of heart disease.
Recovering from a Cardiac Arrest
After surviving sudden cardiac arrest, hospital care is important for recovery and addressing complications. Doctors will monitor heart function and may conduct tests such as electrocardiograms (ECG or EKGs), echocardiograms, or cardiac catheterisation to assess damage and identify underlying issues.
Treatment often involves medications or procedures to manage heart conditions like arrhythmias, coronary artery disease, or heart failure. In some cases, patients may receive an implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) to prevent future cardiac arrests.
Lifestyle changes, such as adopting a heart-healthy diet, exercising regularly, and quitting smoking, are often recommended to lower the risk of recurrence. Many patients benefit from cardiac rehabilitation programs, which focus on improving heart health, rebuilding physical strength, and managing stress or other risk factors.
Emotional recovery is also important, as surviving a cardiac arrest can lead to anxiety, depression, or trauma. Counselling and support groups can provide valuable assistance in managing these challenges. Regular follow-up with healthcare providers ensures a safer recovery and helps prevent future cardiac events.

When it comes to a cardiac arrest, every second counts, Equip yourself with the right skills so you can take action when it matters most. Don’t wait! Join our comprehensive First Aid course and start your journey to becoming a life saver today!
Conclusion
Understanding what causes cardiac arrest, recognising its symptoms, and being equipped with the knowledge to perform first aid can save lives. Considering that it is a serious condition, awareness and swift action can significantly impact survival rates. Always be prepared with the right tools and knowledge.