When it comes to any work environment, safety must be a top priority, especially in industries that deal with hazardous materials, such as flammable and Combustible substances. Knowing the difference between these two types of substances helps prevent workplace accidents and protect people and property. Following basic safety guidelines is essential to keep your team safe and your workplace compliant.
This article will help you clearly understand the key differences between flammable and combustible substances, in simple terms, with easy examples, so you can maintain a safer workplace.
What is a Flammable Substance?
Flammable substances are materials or liquids that easily catch fire, even at normal room temperatures. They have low flash points, which means they can give off vapours that ignite quickly when exposed to a spark, flame, or heat.
Think of petrol or acetone – they can instantly catch fire if not handled or stored correctly.

Did You Know?
Even heat from everyday activities can pose a risk. That’s why understanding how heat affects substances, like knowing the temperature danger zone for food, is crucial to overall workplace safety.
Common Flammable Items:
Flammable fabrics include: cotton, polyester, nylon
Flammable liquids include: petrol, acetone (nail polish remover), ethanol (hand sanitisers)
What is a Combustible Substance?
Combustible substances can also catch fire, but not as easily as flammable ones. They need to be heated to a higher temperature before they begin to burn. Once they catch fire, they can keep burning steadily and fuel a large fire.
Think of materials like wood or paper. They won’t burst into flames immediately, but if there’s enough heat, they will burn and spread fire.
Common Combustible Substance:
Combustible solids include: wood, paper, plastic
Combustible liquids include: Diesel, Vegetable oil, Paint thinner
Even though these materials may appear safe when stored, they can become hazardous if left in large quantities or exposed to heat or fire.
To better understand why, let’s first look at an important concept: Flash Point.
What is a Flash Point?
This is the lowest temperature at which a substance gives off enough vapour to catch fire when exposed to a flame or spark.
In simple words, the lower the flash point, the easier it is to catch fire.
That’s why knowing the flash point of a material helps in understanding how easily it can ignite and how careful you need to be with it.
Flash Points of Flammable and Combustible Substances
Type of substance | Flash Point |
Flammable substance | Below 37.8°C |
Combustible substance | Above 37.8°C and below 93.3°C |
So, what does flash point mean in the workplace?
If a material has a flash point below 37.8°C, it can release flammable vapours even at normal room temperature (usually below 30°C). These vapours can easily ignite, making the material flammable.
On the other hand, materials with a flash point between 37.8°C and 93.3°C won’t usually produce vapours in a typical work setting. That means they are less likely to catch fire under normal conditions, so we call them combustible.
Think of it this way: one liquid starts releasing flammable vapours at room temperature (around 22°C), while another only does that when it gets much hotter, like 70°C. The first one can catch fire more easily, even on a warm day, so it’s called flammable. The second needs more heat to burn, so it’s combustible.
Knowing the flash point of materials in your workplace helps you plan proper storage, reduce fire hazards, and create a safer environment for everyone.
Flash Points of Common Flammable and Combustible Substances
Flammable substances | Flash Point | Combustible substances | Flash Point |
Petrol (Gasoline)* | -43°C | Diesel Fuel* | 52°C to 82°C |
Ethanol | 16.6°C | Phenol | 79°C |
Acetone | -20°C | Kerosene* | 38°C to 72°C |
Methanol | 12°C | Formaldehyde | 64°C |
Propylene Oxide | -37°C | Hydrazine | 52°C |
Ethyl Chloride | -50°C | Paint Thinner* | 40°C |
Benzene | -11°C | Naphthalene | 78.9°C |
Note: this may vary depending on the specific composition
What is the Difference Between Flammable and Combustible Substances?
Let’s now clearly compare flammable and combustible substances to help you take proper safety measures. This will help you identify them more easily in the workplace and help you take appropriate safety measures.
Refer to the visual comparison chart below for a quick breakdown of flammable vs combustible substances.

In Simple Terms:
- Flammable = Lights up fast (e.g., petrol, acetone)
- Combustible = Burns with more heat (e.g., diesel, kerosene)
Why Knowing the Difference Matters at Work
Flammable and combustible materials can seriously impact workplace safety, especially if stored near heat, sparks, or open flames. Some of these materials release vapours that can catch fire or cause explosions if improperly handled.
To avoid these risks, you first should check the Safety Data Sheets (SDSs) of any hazardous material used or stored in your workplace.
What Is an SDS & Why Is It Important?
An SDS (Safety Data Sheet) is a document that tells you everything you need to know about a chemical or substance, including how to handle it safely.
Each SDS includes key details like:
- The substance’s name and the manufacturer’s contact information
- Its physical and chemical properties (like flash point)
- Potential health hazards and fire risks
- Storage and disposal instructions
- First-aid and fire-fighting steps
Tip: Always read the SDS to check whether a substance is flammable or combustible, and follow its recommended safety measures.
How to Reduce Fire Risks at Work
Here are some simple, practical tips to stay safe:
🔥 For Flammable Materials:
- Store in approved, airtight containers to stop vapours from escaping.
- Keep them away from ignition sources — even a small spark can start a fire.
- Use clear labels so everyone knows what they’re handling.
- Ensure proper ventilation to avoid vapour build-up.
- Dispose of waste safely, as leftover vapours can still be a hazard.

♨️ For Combustible Materials:
- Store in a cool, well-ventilated area — heat can raise the risk of ignition.
- Use non-sparking tools like brass or plastic when handling them.
- Avoid heaters, direct sunlight, or machinery that gives off heat.
- Follow local safety guidelines for handling and storage.
Understanding the difference between flammable and combustible substances is essential for workplace safety. Always look for the hazard symbol, especially the flame icon, to identify flammable substances.
Review Safety Data Sheets (SDS) for information such as flash points and handling instructions. These small steps can go a long way in preventing accidents.
Make it a habit to check these every time you handle, store, or dispose of a chemical.
If you work in the food industry, this knowledge becomes even more critical. From cooking oils to cleaning agents, flammable substances are more common than you might think. Mishandling them can lead to serious safety and hygiene risks.
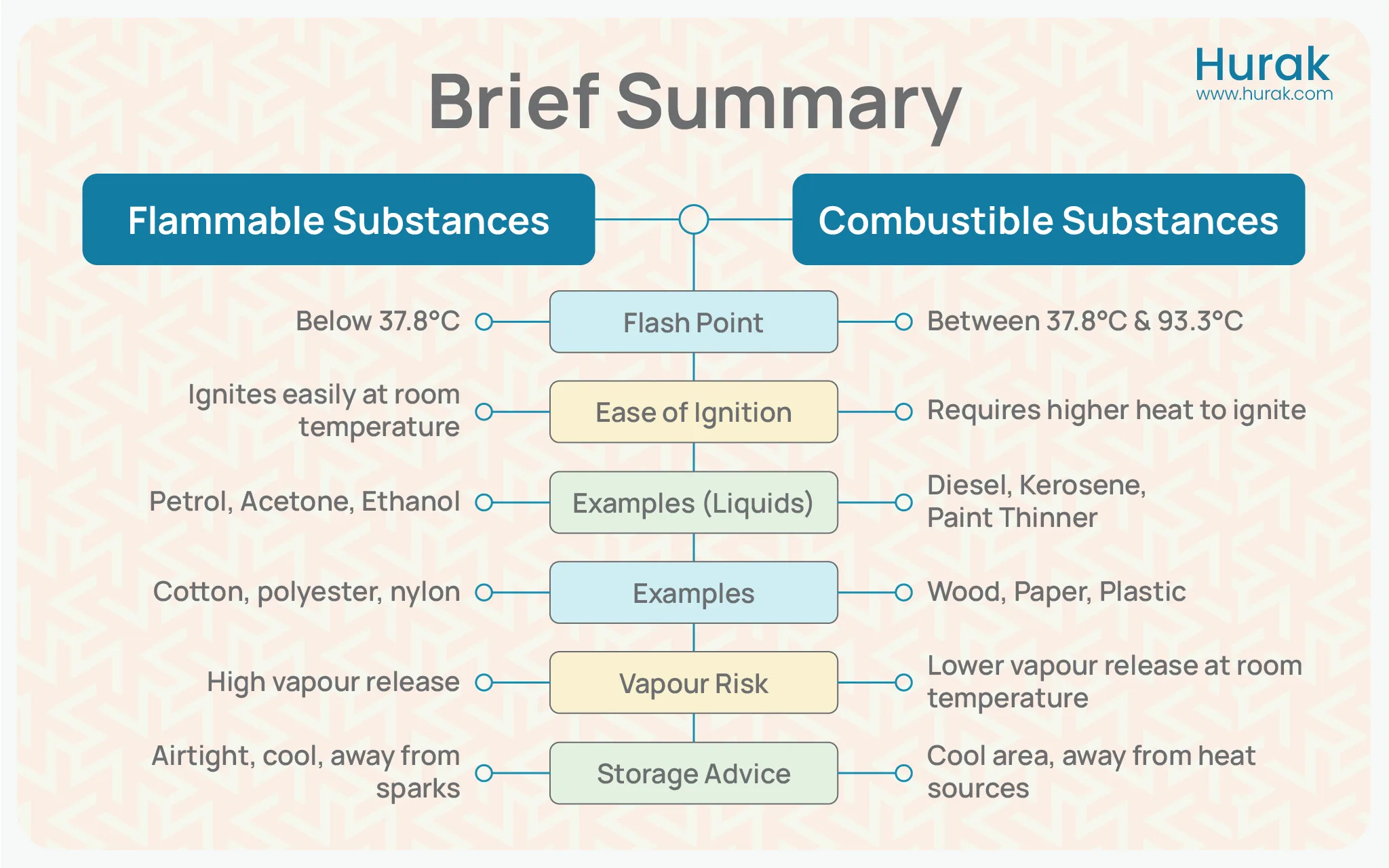
Key Takeaways: Flammable and Combustible Substances
This table highlights the key points covered in the article, offering a quick reference to the main differences between flammable and combustible substances, their flash points, examples, and safety considerations.
Work in Food Safety?
Learn how to manage hazardous materials like oils, chemicals, and more.
Book a Certified Food Safety Course Today →
FAQs
Are flammable and combustible substances the same?
No. Flammable substances ignite at lower temperatures, while combustible ones need more heat to catch fire.
What is a flash point?
It’s the lowest temperature at which a substance gives off vapour that can ignite.
Why is the flash point important?
It helps determine how easily a material can catch fire.
Where can I find flash point information?
Check the Safety Data Sheet (SDS) for any hazardous material.
Is diesel flammable or combustible?
Diesel is combustible. It needs more heat to ignite than petrol.
What’s the difference between flash point and fire point?
The flash point is when the vapour ignites briefly. The fire point is the temperature at which it burns continuously.
Are flammable substances more dangerous than combustible ones?
Yes, because they can catch fire even at room temperature.
Can combustible materials become flammable?
Under high heat or pressure, they can behave like flammable ones.
What makes a substance hazardous in terms of fire?
Low flash point and high vapour production near heat sources.
How can I reduce fire risk from flammable substances?
Store safely, keep away from heat, and follow handling guidelines.





