Every workplace, no matter how big or small, carries some level of risk. Whether it’s slipping on a wet floor, mishandling hazardous materials, or working at height, the potential for harm is always present. That’s why the UK introduced one of its most vital pieces of legislation, the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974 (HASAWA).
This Act is the foundation of all modern health and safety laws in the UK. It was designed to protect not only employees but anyone who could be affected by work activities, including the self-employed, contractors, and members of the public. But HASAWA is more than just legal jargon. It influences how we plan, organise, and carry out our work. In this article, we’ll explore what HASAWA is, how it reformed workplace safety, and why it matters to you, whether you’re an employee, manager, or simply preparing for a new career.
What is the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974?
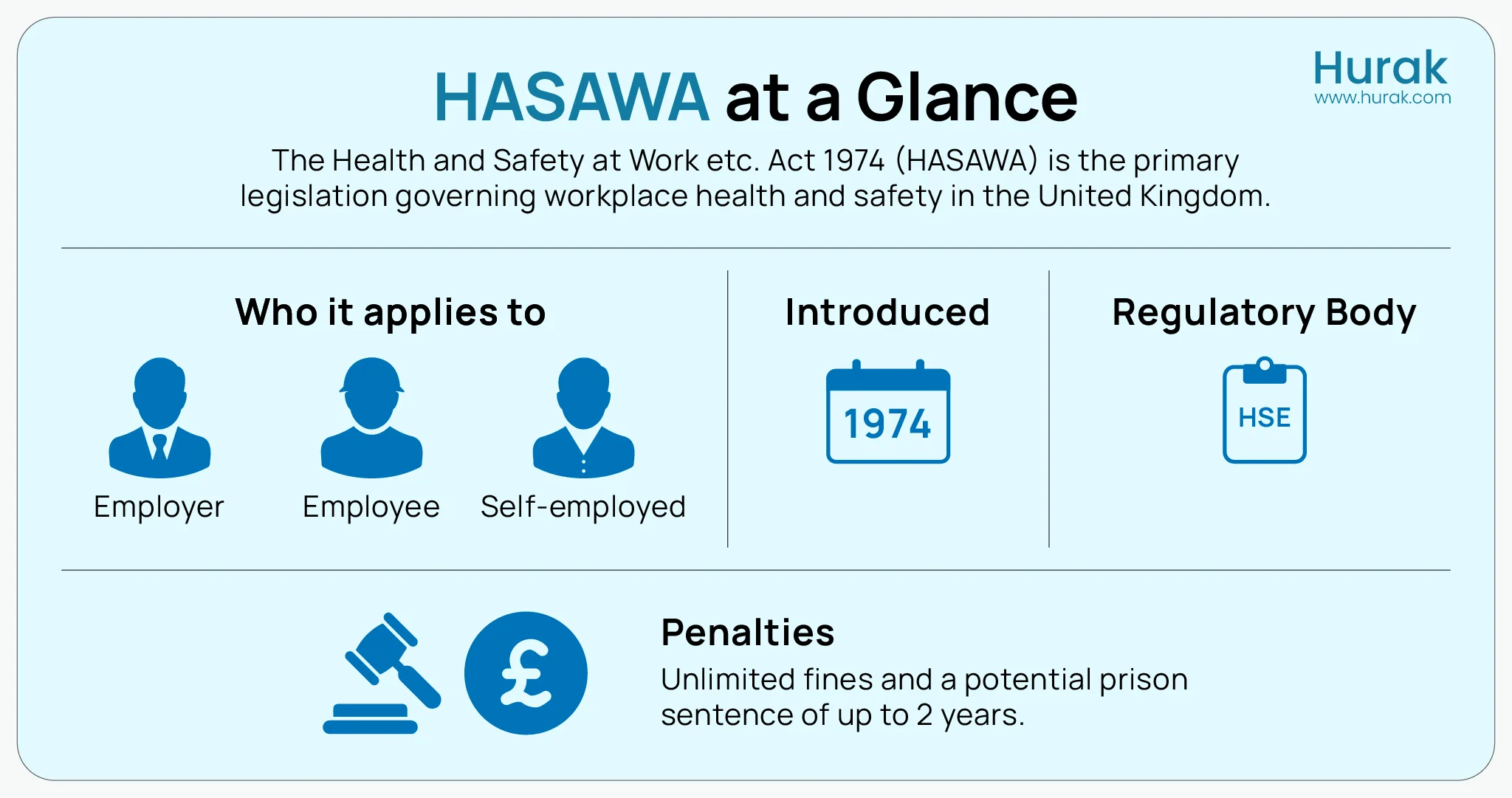
The Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 is the UK’s primary law governing health, safety, and welfare in the workplace. Before HASAWA, safety regulations were scattered and inconsistent; many workers had little or no protection from workplace hazards. This Act brought everything together under one consistent legal framework.
HASAWA applies to nearly all employers, employees, and self-employed individuals in the UK. It outlines a duty of care for all individuals involved in work-related activities. Employers must ensure, so far as is reasonably practicable, the health and safety of their employees. In turn, employees have a responsibility to take reasonable care of themselves and others and to cooperate with their employer’s health and safety arrangements.
What makes HASAWA unique is that it focuses on principles rather than prescribing detailed rules. This enables flexibility and adaptability across various industries, from construction sites to care homes.
When Was the Health and Safety at Work Act Introduced?
The Act was introduced in 1974, during a time when industrial accidents and workplace hazards were significantly more common. Workers in factories, construction sites, and chemical plants faced daily dangers with limited legal protection.
Before HASAWA, UK safety laws were fragmented and industry-specific, creating inconsistencies in standards. The introduction of HASAWA represented a unified, comprehensive approach to workplace safety that could evolve with changing industries and technologies.
What Did HASAWA Change?
It Made Health and Safety Everyone’s Responsibility
One of the most fundamental reforms introduced by HASAWA was the concept that everyone involved in a work activity has a role to play in maintaining a safe workplace. This wasn’t just a legal technicality; it marked a cultural shift.
Employers became legally obligated to protect the health, safety, and welfare of their employees. That includes ensuring that machinery is safe to use, work environments are clean and risk-free, proper training is provided, and safety equipment, such as helmets or harnesses, is both available and adequately maintained. But it didn’t stop there. Employers also have a duty to protect others who may be affected by their work, such as contractors, delivery drivers, customers, or even people passing by a construction site.
Employees, too, were given clear responsibilities. Under Section 7 of the Act, every employee must take care of their safety and that of others who may be affected by their actions. They must follow health and safety instructions, attend training sessions, and use protective gear properly. Deliberately misusing or interfering with safety equipment, like removing a guard from a machine or blocking a fire exit, is a direct offence under Section 8.
This mutual accountability model remains the foundation of workplace safety law today.
It Extended Protection to the Public and Self-Employed
Before HASAWA, safety laws mostly covered traditional employer-employee relationships. The 1974 Act changed that by recognising that work activities often involve people outside the organisation.
If a shop floor is slippery and a customer falls, or if scaffolding collapses and injures a pedestrian, the employer is held responsible under the Act. The law requires businesses to take steps to ensure that non-employees, including clients, visitors, and members of the public, are not put at risk due to work being carried out.
It also recognises the growing number of self-employed people. Under HASAWA, self-employed individuals must ensure that their work doesn’t pose a danger to others. Whether you’re a freelance electrician or a self-employed cleaner, you’re still legally required to carry out risk assessments and use equipment safely.
This reform ensured that safety isn’t limited by job title; if your work impacts others, you’re part of the system.
📖 Related reading: Consequences of Poor Health and Safety Procedures
It Introduced the Health and Safety Executive (HSE) for Enforcement
Legislation is only helpful if it’s enforced. HASAWA addressed this by establishing the Health and Safety Executive (HSE), a dedicated national regulator for workplace safety. The HSE has the authority to investigate workplaces, enter premises without warning, and ensure compliance.
If they find serious risks or breaches, they can:
- Issue improvement notices requiring fixes by a set date
- Serve prohibition notices that stop work immediately.
- Prosecute companies and individuals in court.
Fines under the Act can be unlimited, and in severe cases, company directors or managers can face up to two years’ imprisonment. This enforcement mechanism made it clear that health and safety are not optional; it’s a legal and moral responsibility.
If you’re stepping into a leadership role, understanding your obligations is critical. The IOSH Managing Safely course is designed to help professionals navigate these legal duties with confidence.
Regulations That Support HASAWA
HASAWA outlines general duties, but its flexibility is further enhanced by supporting regulations that provide specific, actionable guidelines. These regulations are legally binding and help employers interpret and apply HASAWA in real-life situations.
- The Management of Health and Safety at Work Regulations 1999 require employers to carry out detailed risk assessments, introduce emergency procedures, and appoint competent persons to oversee safety.
- The Control of Substances Hazardous to Health (COSHH) Regulations 2002 provide guidance on the safe storage, handling, and disposal of chemicals, dust, fumes, and other hazardous substances. These rules are especially critical in labs, cleaning roles, and manufacturing sectors.
- The Provision and Use of Work Equipment Regulations (PUWER) 1998 ensure that all tools and machines used in the workplace are safe and maintained. Employers must check that staff are trained before using such equipment.
- The Manual Handling Operations Regulations 1992 address one of the most common workplace injuries, musculoskeletal damage from lifting or moving objects. Employers must reduce the need for manual handling and train staff in safe techniques.
- The Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005 focuses on fire risk assessment, emergency exits, fire alarms, and staff training. Fire safety responsibilities fall on a “responsible person,” often the employer or building manager.
For those responsible for teams or compliance, a more advanced understanding of legal duties is essential.
🧠 Managing People or Projects? Know Your Legal Responsibilities.
The IOSH Managing Safely course helps team leaders and managers confidently and effectively comply with health and safety law.
Why This Act Still Matters Today
Although the HASAWA was introduced in 1974, it remains the backbone of workplace safety in the UK. The nature of work has changed dramatically, offices have gone remote, new technologies have emerged, and mental health has taken centre stage. Yet the Act’s flexible, principle-based approach means it remains applicable.
Understanding your responsibilities under HASAWA isn’t just about avoiding fines or ticking boxes. It’s about being a better professional. You become more aware of your environment, more conscious of risks, and more proactive in solving problems before they escalate. These are qualities that employers value highly, especially in roles related to leadership, operations, facilities, or HR.
Conclusion
The Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 revolutionised the way we think about safety at work. It imposed a legal duty on employers to protect others, made safety a collective responsibility, and established a system of enforcement to hold individuals accountable for their actions. But beyond legal compliance, this Act is about culture; it encourages every person in the workplace to be aware, to act, and to care.
Whether you’re wearing a hard hat or managing a team from a desk, your understanding of HASAWA can make the difference between a safe, supportive environment and a risky one. In the modern world of work, that knowledge is not only empowering but also essential.
Thinking about stepping into a leadership or compliance role? This course provides in-depth knowledge and credibility.
🎓 Looking to Advance Your Career in Safety Compliance?
The Level 3 Health and Safety (RQF) qualification is ideal for professionals stepping into supervisory or compliance-focused roles.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974?
It’s the UK’s main law protecting workplace health, safety, and welfare. It outlines the legal duties of employers, employees, and others involved in work activities.
What does HASAWA 1974 mean?
HASAWA refers to the Health and Safety at Work etc. Act 1974. It ensures all workplaces manage risks and promotes a shared responsibility for safety.
Who does HASAWA place legal duties on?
Employers, employees, self-employed workers, and equipment suppliers all have responsibilities under the Act.
When was the Health and Safety at Work Act introduced?
The Act was introduced in 1974 to address rising workplace accidents and unify outdated safety laws.
What is the main piece of legislation for health & safety in the UK?
The Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 is the central law, supported by specific regulations like COSHH and the Management Regulations (1999).
What is the Health and Safety at Work Act 1974 summary?
It requires employers to protect health and safety, employees to cooperate, and HSE to enforce the law through inspections and penalties.
What law regulates health and safety in the workplace?
HASAWA 1974 is the primary legislation, backed by detailed rules covering chemicals (COSHH), manual handling, equipment use, and fire safety.
How to Build Your Knowledge and Stay Compliant
Whether you’re an employee or in a supervisory role, there are structured training programmes that help you understand and apply HASAWA principles in your day-to-day work:
- Level 3 Health and Safety RQF: Ideal for team leaders or those with compliance responsibilities.
- CITB Temporary Works Supervisor Course: Designed for those managing temporary structures on construction sites.
- Part P Domestic Installers Course: Mandatory for anyone doing electrical work in domestic premises.
You can also browse all available health and safety training to find the right course for your sector or job role.





