Ideally, do not reheat food more than once. However, under appropriate conditions, food reheated two or three times is safe to eat. When it comes to reheating leftover food more than once, whether they are home-cooked meals or dine-in takeaways, appropriate heating and storage temperatures play an important role in determining food safety.
The Safety of Reheating Food
Food reheated more than once is safe if correct temperatures and proper handling conditions are followed. Although fresh food is ideal, you can safely reheat it at an appropriate temperature, using proper storage methods and suitable cooking tools.
How Many Times Can You Reheat Food?
It is best to eat fresh food, right after it comes out of the oven or off the stove. Food should be reheated only once, as suggested by the Food Standards Agency (FSA).
If you are unsure about the odour, texture or palatability of leftover food, it is best to dispose of it. Reheating should not be done quite frequently.
Each time food is reheated, its safety and quality becomes questionable. However, by following certain guidelines reheated meals can be enjoyed without concerns about food safety.
Do not Reheat These Foods More Than Once
It is safe to reheat most foods more than once under suitable temperature and storage conditions. However, there are certain foods that should not be reheated more than once. This is because frequent reheating, even if done properly, negatively affects their taste, quality, texture and overall safety. Examples of foods that should not be reheated more than once include:
- Prawns
- Fish
- Milk
- Cheese
- Custard
- Cooked Rice
- Gnocchi
- Soups
The Safe Method to Reheat Food Leftovers
The safe method to reheat food leftovers requires knowledge about the correct reheating temperature, refrigeration conditions and suitable reheating equipment.
Safe Reheating Temperature and Duration for Food Leftovers
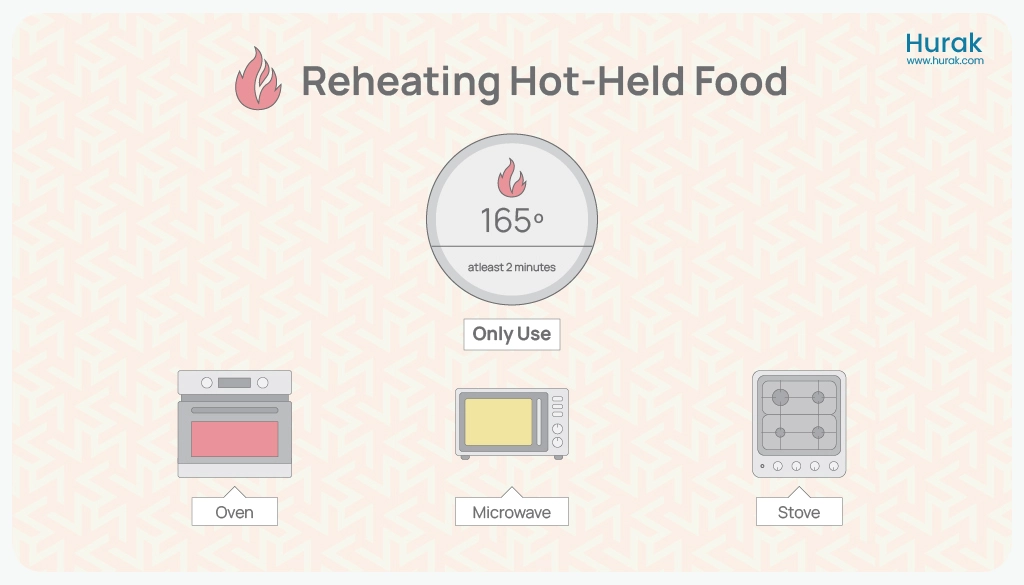
It is preferable to reheat food at 165°F (74°C) for a duration of at least 2 minutes.
Achieving proper internal temperature of food to kill any bacterial growth that may have occurred during storage is the most important aspect of reheating food safely.
Food safety guidelines in England require reheated food to reach an internal temperature of at least 70 °C (158°F). In Scotland, a minimum reheating temperature of at least 82 °C (180°F) is allowed.
Safe Fridge and Freezer Storage for Food Leftovers
Stored food must be kept refrigerated at below 5°C and frozen between 0°C and -18°C. Leftover cooked food can be stored safely for up to 3 to 4 days, with some exceptions. Any unconsumed portions of food must be stored within 2 hours.
Proper refrigeration and freezer storage of food can help preserve food to maintain its safety and hygiene.

Safe Reheating Equipment for Food Leftovers
Food should be reheated to the ideal internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) on air fryers, stovetops, microwave ovens and conventional ovens. It is important to note that slow heating devices are not recommended for reheating leftovers.
Reheating Food in an Air fryer
Air fryers are a recent invention in the world of cooking that serve dual purposes of cooking and reheating. While reheating food in an air fryer, set the temperature to 350°F (175°C) and reheat food for a few minutes. Check that its internal temperature reaches 165°F (74°C). Allow frequent stirring for proper heating. Air fryers provide convenience for preserving flavour and moisture content of your reheated food.
Reheating Food in a Slow Cooker
Slow heating devices, such as a slow cooker, are not recommended for reheating leftovers. It carries the risk of food remaining over-exposed to temperatures in the danger zone, between 40 °F and 140 °F. The danger zone temperature increases the growth rate of food bacteria.
Reheating Food in Conventional Ovens, Microwave Ovens and Stovetops
Conventional ovens reheat food evenly but may take longer than other heating devices. Reheating in microwave ovens requires periodic stirring for even heating. Accurate temperature control can be achieved with stovetops but may demand our undivided attention.
Defrosting and Reheating Frozen Food
Completely defrost frozen food before reheating, by placing it from the freezer to the fridge, kept at a temperature range of 0°C- 4°C. It is not recommended to defrost food at room temperature or in a microwave. This is to avoid exposure to undesirable temperatures that promote bacterial growth in food.
Reheating Frozen Food Twice
Once frozen food has been thawed, it is recommended to reheat it only once to prevent the risks of spoilage and microbial contamination. However, frozen food can be reheated more than once provided that it is thoroughly heated to an internal temperature of 165°F (74°C) to completely destroy harmful bacteria.
Probe Thermometer to Check Food Temperature
The reading on the thermometer will indicate whether the food has undergone any contamination or spoilage due to bacterial growth. Check temperature using an appropriate metal stem probe thermometer to detect microbial spoilage in food.
Safe Reheating of Food for Children
The NHS suggests that reheating cooked food for a child should only be done once. Microwaved food should be stirred properly to avoid any air pockets before feeding the baby. While reheating, food must be hot and cooled before serving.
Refrigerating Food Leftovers
Reheated food must be allowed to cool properly before storage. For rapid cooling, food can be placed in an ice bath and chilled before placing it in the fridge.
Common Risks of Reheating Food
Common risks concerned with reheating food include inappropriate temperatures leading to uneven heating and if the food has been stored at room temperature for a prolonged period of time. These risks lead to food poisoning, anti-palatability and consumer dissatisfaction.
Inappropriate Temperatures and ‘Hot Spots’
If food is reheated at an incorrect temperature, certain parts of food reach higher temperatures than others. This creates ‘hotspots’ that act as breeding grounds for food pathogens. Pockets of hot and cold portions of food can also lead to an unsatisfactory taste and lack of appetite for the meal.
Prolonged Storage at Room temperature
The chances of bacterial contamination increase if food is stored at room temperature for a prolonged period of time. At room temperature, food is susceptible to ‘Danger Zone’ temperatures between 40°F (4°C) and 140°F (60°C). At these temperatures, bacteria thrive and multiply, leading to food spoilage.
Food poisoning and Consumer Health Impacts
A negative consequence of consuming unsafe reheated food is food poisoning, due to entry of pathogens such as Campylobacter and Salmonella into the human body. Common symptoms of food poisoning include nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, and in severe cases, hospitalisation or even death.
Impact on Commercial Food Products
Food reheating and storage protocols are important to uphold the reputation and popularity of a food business. If customers face health concerns due to low food quality, the demand for the food product can decline. This can result in financial losses for the food company. For consumer loyalty and trust, safe food reheating and storage guidelines should be followed.
Common Mistakes in Reheating Food
Several common mistakes can compromise the safety and quality of reheated food. These include use of plastic or metal containers, reheating food at incorrect temperatures, and uneven heating.
Use of Plastic or Metal Containers
Plastic containers, when exposed to high temperatures, can pass on undesirable chemicals to food. Sparking can occur on uneven heating with metal containers. It is preferable to use ceramic or microwave safe-glass containers to heat food evenly, to avoid chemical leaching.
Reheating Food at Inappropriate Temperatures
The appropriate temperature to reheat food is at least 165°F (74°C) to destroy bacterial growth. If reheated at an inappropriate temperature, any bacteria present in food will not be completely destroyed. This increases the risk of food poisoning. It is recommended to use a food thermometer to make sure that food has achieved desirable reheating temperatures.
Lack of Stirring for Even Heating
When one does not stir food properly while reheating, some portion of food may become burnt while the rest would be left under-heated. This reduces palatability and promotes microbial growth in food. Constant stirring while reheating helps distribute heat evenly throughout the food, confirming food hygiene.
Get Online Food Safety Courses
Food Hygiene And Safety
Check the CourseRated Excellent
on major review sites

When to Discard Reheated Food?
Sometimes bacterial activity can cause contamination in food that undergoes proper reheating. Unusual flavours, odours and texture are signs of discarding the reheated food and it’s best not to eat it.
Odour
The most prominent sign of spoilage is foul and unusual odour which could imply chemical changes in food due to bacterial contamination.
Flavour
Uncharacteristic or sour flavour of food that is different from its original taste is another sign of food spoilage due to bacterial activity.
Texture
If reheated food has become slimy or semi solid in nature, indicating unusual consistency of food, the reheated food must be discarded immediately.
It is best to practise vigilance when examining reheated food before eating it. Carefully identify the signs of food spoilage in terms of foul odour, uncharacteristic flavour and inconsistent texture. Even if reheated under desirable conditions, reheated food can still become inedible due to microbial pollution.
Can You Reheat This Food More Than Once?
Cooked Rice
It is not recommended to reheat rice more than once. Rice must not be stored in the fridge for more than a day. While reheating cooked rice, add a small quantity of water and heat it in a microwave, checking its consistency with a fork. This will prevent rice from becoming dry or lumpy.
Chicken
Use of a low-temperature oven when reheating chicken maintains its stable water content. To retain the original flavour of the meat, cover it with an aluminium foil to retain moisture.
Stir-fry
In a frying pan, reheat the stir-fry chicken using a small amount of oil for 2-5 minutes, with continuous stirring.
Conclusion
Reheating food leftovers more than once can be safe if proper precautions are taken. While it’s best to eat food fresh, reheating can be done safely at the correct reheating and storage temperatures. Using suitable reheating equipment and even heating of food are other measures that allow people to enjoy leftover meals without worrying about food safety.




