An effective food safety management system includes the principles of HACCP, TACCP, and VACCP. Generally, food safety is maintained through HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Points), which manages potential hazards arising from processing errors or human mistakes.
However, there has been a rise in threats involving deliberate tampering or contamination of food for malicious or financial reasons, which are not specifically addressed by HACCP.
As an ethical and legal strategy to fulfil high food safety and hygiene standards, TACCP and VACCP complement HACCP in maintaining food safety across the entire supply chain. Both strategies focus on preventing food adulteration.
What Does TACCP Stand For?
TACCP stands for “Threat Assessment and Critical Control Point.” It is a food safety management approach used to identify and assess potential food safety threats not covered by traditional HACCP (Hazard Analysis Critical Control Point) systems.
What is TACCP?
While HACCP focuses on managing known hazards, TACCP addresses more specific and often less predictable threats, such as deliberate contamination or sabotage. By including TACCP, food businesses can better safeguard their products from unintentional and intentional risks.
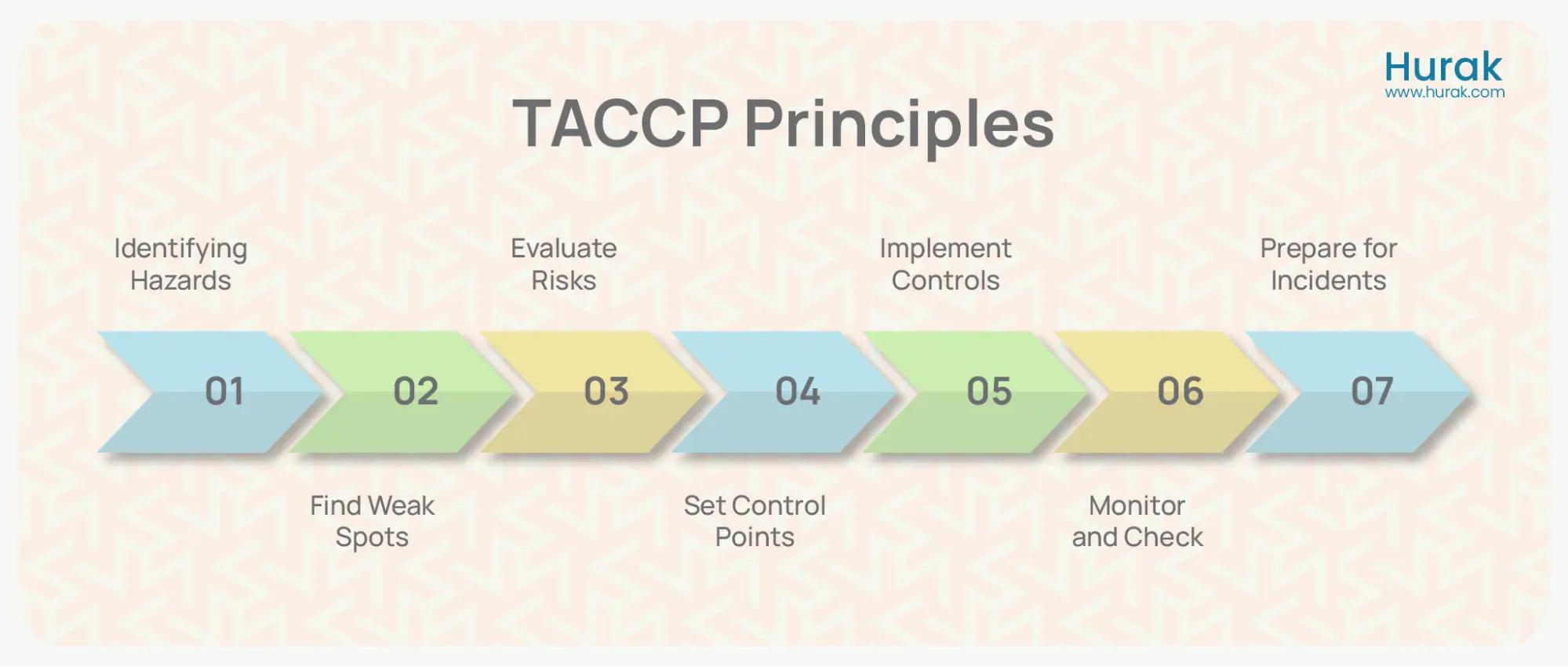
What are the TACCP Principles
The principles of TACCP (Threat Assessment and Critical Control Point) are:
- Identify Threats: Find out what intentional harm could happen to food, like sabotage or fraud.
- Find Weak Spots: Examine the production process and supply chain to see where these threats could enter.
- Evaluate Risks: Consider how likely these threats will be used and how easily they can exploit the weak spots.
- Set Control Points: Choose key areas where you can implement measures to prevent or stop the threats.
- Implement Controls: Put security measures in place to address the threats, such as better storage or surveillance, and train staff to spot problems.
- Monitor and Check: Regularly check if the controls are working and update them as needed based on new information or changes in risks.
- Prepare for Incidents: Prepare a plan for responding to an intentional contamination incident, including who to contact and what actions to take.
What is an Example of TACCP?
To explain how TACCP works in food safety, we can use the example of a small-town bakery.
The bakery’s team starts the TACCP process by checking for possible threats, such as contamination of ingredients like flour. They then identify vulnerable points in the production process and assess how likely these vulnerabilities will be exploited. The bakery implements security measures to reduce these risks, such as secure ingredient storage and surveillance. The staff is trained to detect and respond to suspicious activities. By proactively addressing potential threats, the bakery successfully prevents deliberate contamination.

What does VACCP Stand For?
VACCP stands for “Vulnerability Assessment and Critical Control Points.” It is a food safety approach focused on identifying and managing vulnerabilities in the food supply chain that could lead to food fraud and financial loss.
What is VACCP?
VACCP is a type of risk assessment that helps find and manage weaknesses in the food supply chain that could lead to food fraud for financial gain. VACCP aims to prevent intentional fraud, where food is deliberately tampered with during production for economic reasons.
In a VACCP assessment, a food business examines its processes and supply chain to identify potential food fraud. This helps the business understand and address specific types of fraud.
Food fraud involves tricking customers or consumers for financial benefit. VACCP focuses on preventing two key types:
- Adulteration: Adding something not listed on the label to reduce costs or fake a higher quality.
- Substitution: Replacing a food or ingredient with a similar but lower-quality substance.
Get Online Food Safety Courses
Food Hygiene And Safety
Check the CourseRated Excellent
on major review sites

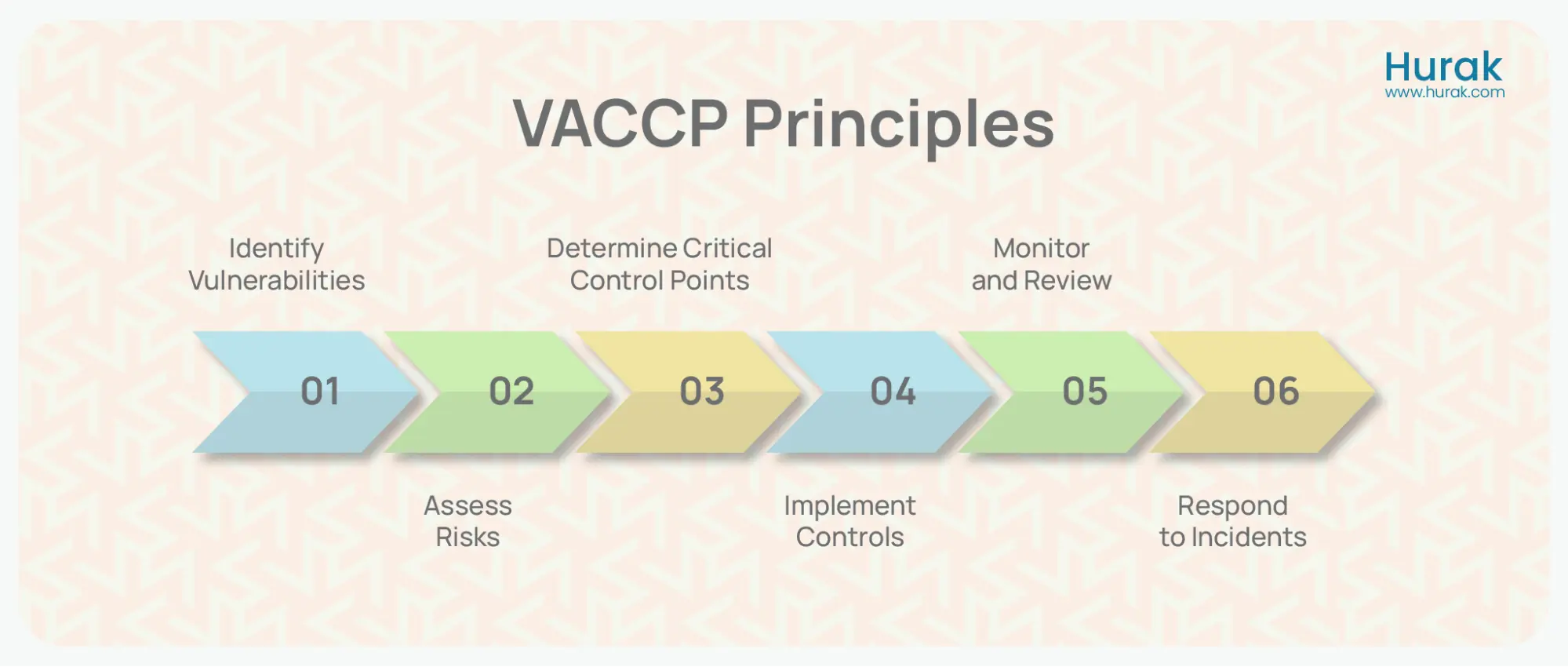
What are the VACCP Principles?
The principles of VACCP (Vulnerability Assessment and Critical Control Points) are:
- Identify Vulnerabilities: Recognise production and supply chain areas where food fraud could occur.
- Assess Risks: Evaluate how likely these vulnerabilities could be targeted and the potential impact of such fraud.
- Determine Critical Control Points: Identify key stages where controls can be applied to prevent or detect food fraud.
- Implement Controls: Put in place measures to address the identified vulnerabilities and risks.
- Monitor and Review: Regularly check the effectiveness of the controls and review the vulnerability assessment.
- Respond to Incidents: Have a clear plan for addressing food fraud incidents, including investigation procedures and corrective actions to prevent recurrence.
What is an Example of VACCP?
We can use a juice manufacturing company as an example to explain how VACCP works in the food industry.
In a juice manufacturing company, VACCP is used to combat food fraud by focusing on supply chain vulnerabilities and production processes. The company identifies risks such as the potential substitution of high-quality fruit concentrates with cheaper alternatives and the threat of counterfeit packaging. They implement controls like quality checks on ingredients and tamper-evident packaging. Regular monitoring and audits are conducted to ensure these measures are effective. If fraud is detected, the company follows a response plan to trace the source, notify affected parties, and prevent future incidents. This approach helps maintain the integrity and authenticity of their products.

What is the Difference between TACCP & VACCP
TACCP and VACCP aim to prevent intentional food contamination, unlike HACCP, which deals with unintentional contamination. VACCP targets system vulnerabilities, focusing on where weaknesses could be exploited for fraud.
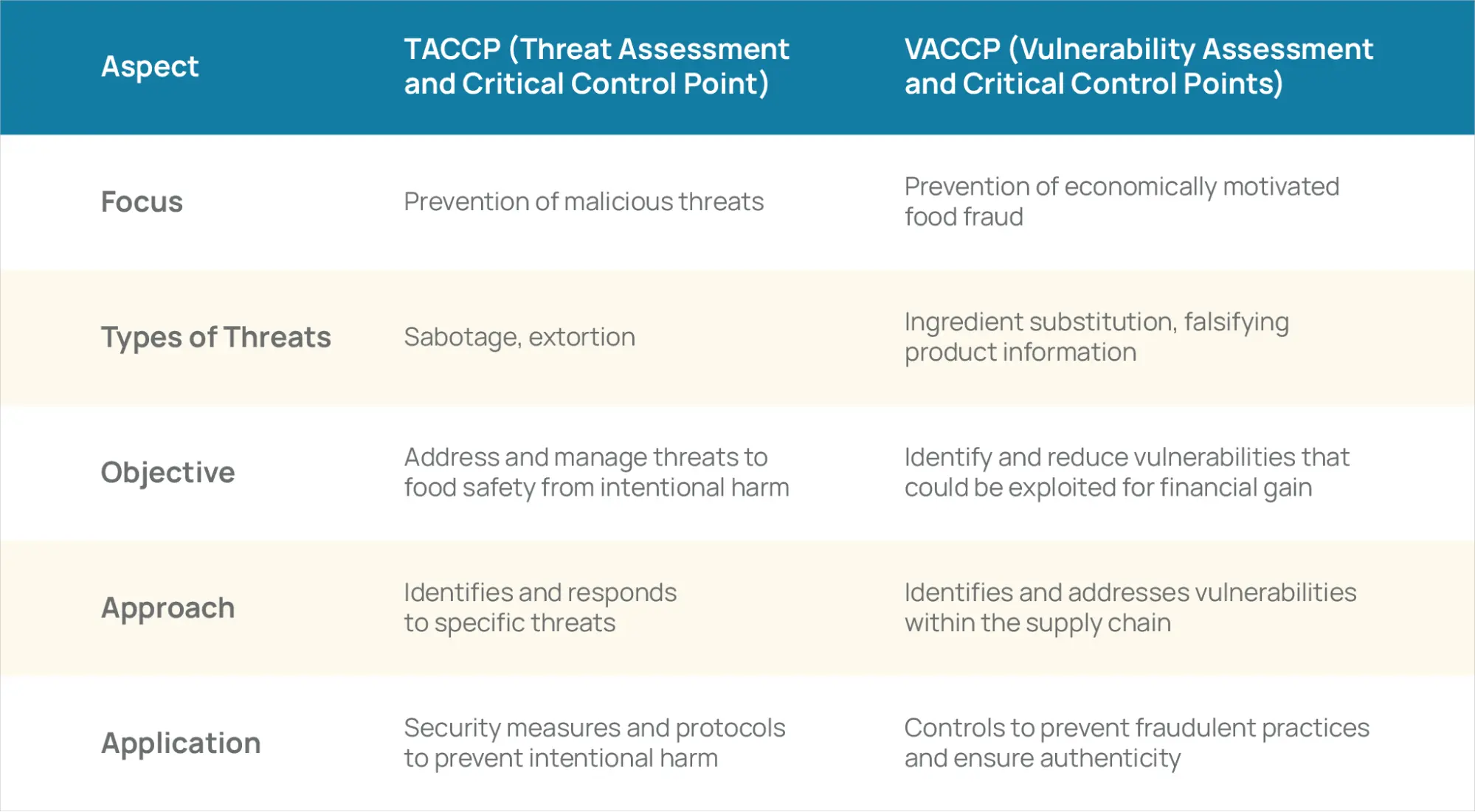
In contrast, TACCP identifies specific threats, concentrating on what could happen. Essentially, TACCP is concerned with the nature of the threats, while VACCP addresses the timing and opportunity for fraud.
TACCP and VACCP focus on identifying and preventing potential adulteration in the food supply chain but address different threats. TACCP aims to prevent malicious threats such as sabotage or extortion. In contrast, VACCP focuses on preventing food fraud driven by economic motives, like substituting ingredients or falsifying product information for financial gain.
What are the Benefits of TACCP and VACCP?
Using TACCP and VACCP in a food business offers several advantages:
- Shows your commitment to food safety
- Lowers the risk of intentional attacks or fraud
- Ensures reasonable precautions are taken to protect the supply chain
- Assures stakeholders and customers that risks are managed properly
- Minimises the impact of any attack on your business
- Protects and improves your brand and reputation
Conclusion
TACCP and VACCP are strong defences against food fraud and contamination. When used correctly, they help reduce the chances of attacks and lessen the damage if they occur. Together with HACCP, they confirm food safety and protection from intentional and unintentional contamination.




