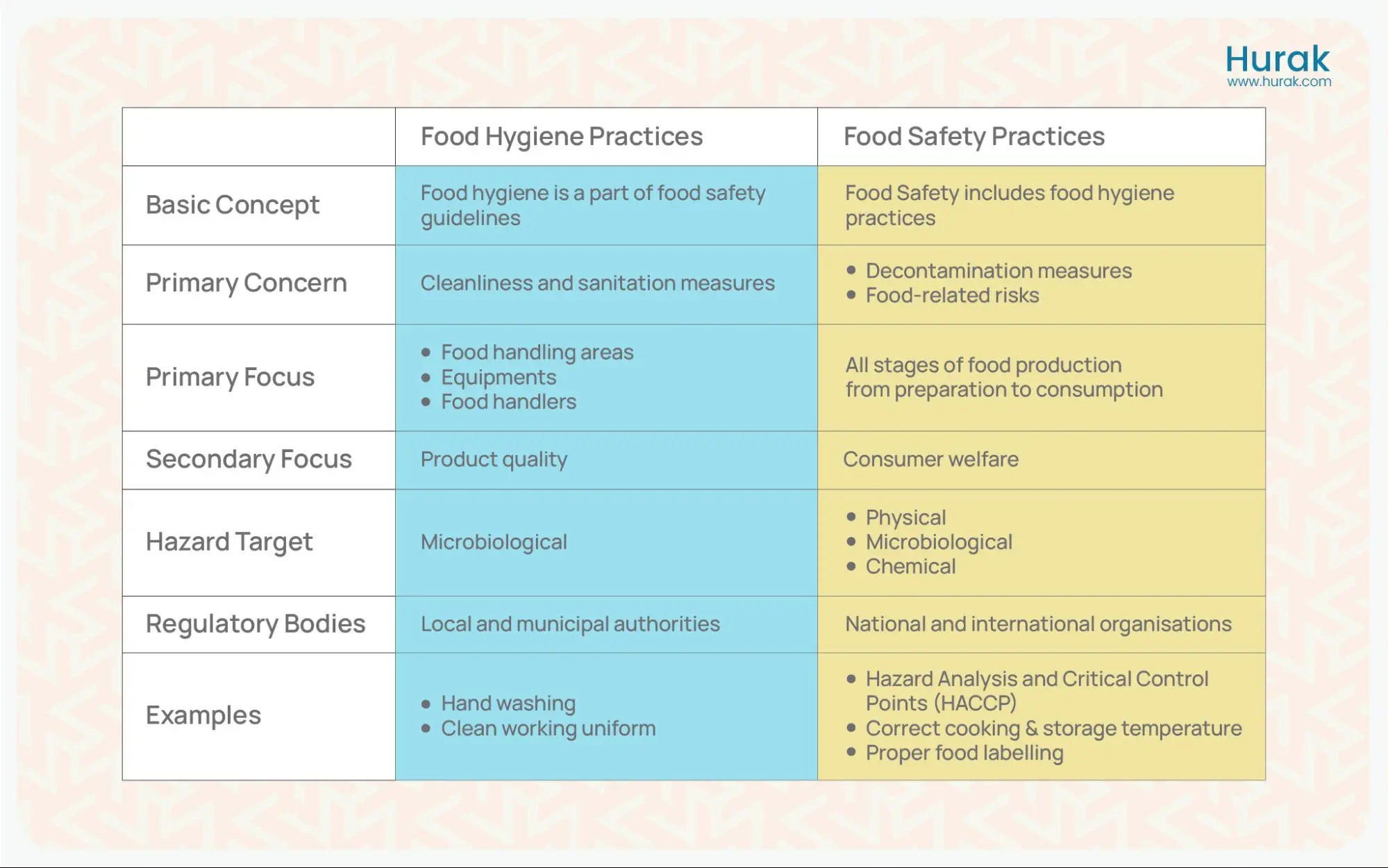
Food safety and hygiene cannot be used interchangeably as they have key differences in meaning and practice. Food hygiene is based on sanitation and cleanliness practices. Food safety is a holistic guide that upholds consumer protection from foodborne hazards. Food hygiene can be considered as part of the complete food safety procedure.
The Main Difference between Food Hygiene and Food Safety
Food hygiene confirms product value and quality. It deals with measures that maintain equipment and facilities cleanliness and proper hygiene. For hygienic food production, washing hands and sanitising surfaces is important. Food hygiene practices prevent bacterial contamination and promote food safety.
On the other hand, food safety is largely concerned with consumer welfare and protecting food from physical, chemical, and microbial contaminants. It involves complete food supply chain safety by following good manufacturing and storage practices. Examples include cooking and storing food at suitable temperatures and protecting food from cross-contamination.
Food Safety & Food Hygiene with Examples
Primary Concern of Food Safety Practices
The primary concern of food safety practices is the prevention of contamination at all stages of the food supply chain.
- Example: In agricultural food production, farmers implement Good Agricultural Practices (GAPs) to minimise the risk of contamination. This includes proper irrigation practices, pest management strategies, and worker hygiene protocols.
Primary Concern of Food Hygiene Practices
Food hygiene practices aim to prevent microbial contamination. They help maintain a clean environment in food handling areas, including kitchens, restaurants, and food processing facilities. This involves maintaining the cleanliness of surfaces, equipment and employees.
- Example: In a restaurant kitchen, food hygiene practices may include regular handwashing by food handlers. They also include proper cleaning and sanitising of food contact surfaces.
Target Hazards in Food Safety Practices
The main types of hazards encountered in food safety are microbiological, chemical, and physical. Microbiological hazards refer to harmful bacteria, viruses, parasites, and fungi that can contaminate food and cause illness.
Chemical hazards include substances such as pesticides, cleaning agents and food additives. Physical hazards are foreign objects like glass, metal, or plastic that can accidentally end up in food products.
- Example: A microbiological hazard could be the presence of Salmonella bacteria in raw poultry, which can cause food poisoning if not properly cooked. Chemical hazards may include pesticide residues on fruits and vegetables. Physical hazards could be pieces of broken glass in a jar of salsa.
Target Hazard of Food Hygiene Practices
Food hygiene practices specifically target microbiological contamination of food that can cause foodborne illness. This requires maintaining strict hygiene practices and sanitation standards to reduce the risk of contamination.
- Example: Pest control measures are implemented to prevent food contamination by insects or rodents, which can act as microorganism carriers.
Standard Regulation of Food Safety Practices
Governments and international organisations establish regulations and standards to ensure food safety and protect public health. These regulations cover food labelling, hygiene practices, and inspection requirements.
- Example: The Food Standards Agency (FSA) is responsible for food safety and hygiene in England, Wales and Northern Ireland.
Standard Regulation of Food Hygiene Practices
Local health departments and municipal authorities enforce regulations and standards for food hygiene practices within their jurisdiction. These regulations may include requirements for food handler training, facility inspections, and pest control measures.
- Example: Health inspectors conduct routine inspections of food establishments to oversee compliance with hygiene regulations. They may inspect food handling practices, cleanliness of facilities and storage of food products.
Key Food Safety Measures
Key measures of food safety include cooking foods to appropriate temperatures to kill harmful bacteria, conducting hazard analysis, and testing food products for contaminants.
- Example: The Hazard Analysis and Critical Control Points (HACCP) system is a preventive approach food businesses use to identify and address potential hazards. This involves conducting a hazard analysis, establishing critical control points (CCPs), and implementing control measures.

Key Food Hygiene Measures
Key measures for maintaining food hygiene include personal hygiene practices among food handlers, such as proper cleaning and sanitation of equipment and facilities. Pest control management is also an important step in food hygiene.
- Example: Food handlers must wash their hands frequently, especially after handling raw meat or using the restroom, to prevent the spread of bacteria.
- Equipment used for food preparation is cleaned and sanitised regularly to remove any traces of food residue or microbial contamination.
- Sealing cracks and crevices is done to prevent the entry and spread of pests carrying microbes in food-handling areas.
Get Online Food Safety Courses
Food Hygiene And Safety
Check the CourseRated Excellent
on major review sites

Conclusion
While food safety and hygiene are essential aspects of food quality and safety, they cannot be used interchangeably. Food hygiene primarily focuses on maintaining cleanliness and sanitation in food handling environments to prevent microbial contamination. On the other hand, food safety has a broader scope, aiming to protect consumers from all harmful contaminants and food-related diseases throughout the entire food supply chain.




