Fear of spiders is one of the most common phobias, affecting people of all ages and backgrounds. Have you ever felt your heart race or your skin crawl at the sight of a spider, no matter how harmless it seemed? You’re not alone. For some, this reaction is mild, but for others, it can trigger intense anxiety that disrupts daily life. Understanding why spiders cause such strong emotions, what drives this fear, and how it can be treated is the first step toward overcoming arachnophobia and feeling more in control.

What is Arachnophobia?
Arachnophobia is an intense, irrational fear of spiders and other arachnids, such as scorpions. It is classified as a specific phobia, meaning the fear is focused on a particular object or situation. While many people feel uneasy or uncomfortable around spiders, arachnophobia goes much further.
People with this phobia often experience overwhelming anxiety at the thought, sight, or even image of a spider. This reaction isn’t simply dislike; it can trigger panic attacks, sweating, rapid heartbeat, and an urgent need to escape. In some cases, the fear is so severe that individuals avoid activities or places where they might encounter spiders, such as basements, garages, or gardens.
Arachnophobia is one of the most common animal-related phobias worldwide. Researchers believe this fear may have evolutionary roots, as early humans needed to avoid venomous spiders for survival. However, in modern life, most spiders pose no real threat, which is why arachnophobia is considered disproportionate to any actual danger.
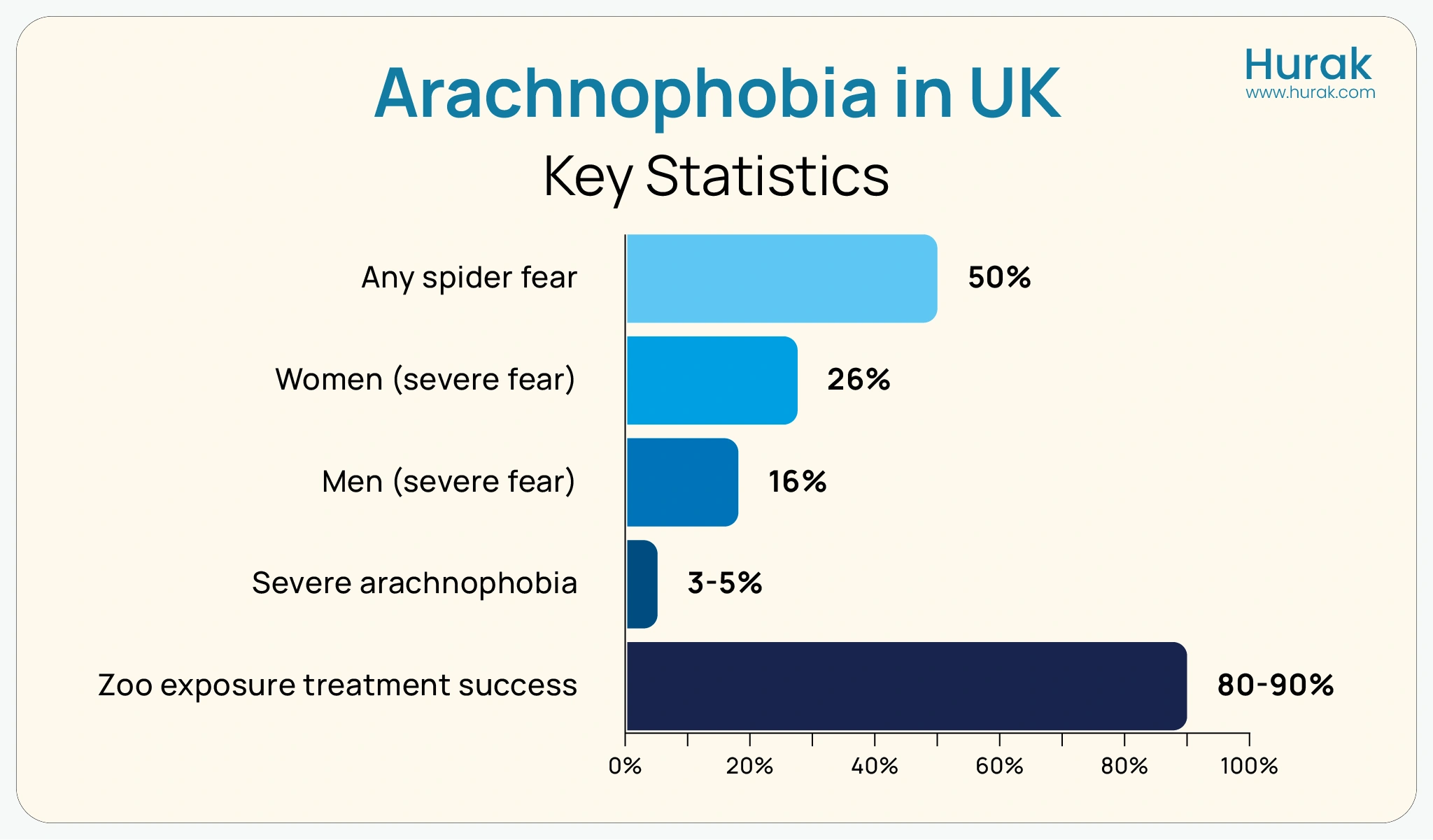
While arachnophobia can feel overwhelming, it is a treatable condition. With the right strategies, support, and therapy, many people successfully learn to manage or overcome their fear of spiders.This infographic highlights key statistics about arachnophobia in the UK, revealing how widespread the fear of spiders is across the population. It compares the prevalence of mild to severe spider fears, shows notable differences between men and women, and illustrates the high success rates of exposure-based treatments offered in zoo programs.
This infographic highlights key statistics about arachnophobia in the UK, revealing how widespread the fear of spiders is across the population. It compares the prevalence of mild to severe spider fears, shows notable differences between men and women, and illustrates the high success rates of exposure-based treatments offered in zoo programs.
Why Are People Scared of Spiders?
Fear of spiders is very common, and often surprisingly intense. While some people only feel mild discomfort, others experience full-blown panic even when a spider poses no real danger. There are several reasons why spiders can trigger such strong reactions:
- Evolutionary Instincts: Humans are thought to have evolved a natural wariness of creatures that could be venomous. In early human history, avoiding potentially dangerous animals, including spiders, was crucial for survival. Even today, this instinctive fear can be triggered automatically, whether or not the spider is harmful.
- Negative Past Experiences: A frightening or unexpected encounter, like a spider crawling on your skin or suddenly appearing close by, can create a lasting association between spiders and danger. This learned fear can resurface whenever you see or think about spiders again.
- Cultural Influences and Media: portrayed as menacing or deadly. These exaggerated depictions can shape our perceptions from a young age, making spiders seem far more threatening than they are.
- Appearance and Movement: Spiders have features that many people find unsettling: multiple legs, fast and unpredictable movements, and unusual body shapes. These characteristics can automatically trigger a fear or disgust response.
- Learned Behaviour: Children often acquire fears from their parents or caregivers. If a parent reacts with panic to a spider, a child can internalise that response as normal or necessary.
Are you afraid to get into these phobias like Arachnophobia?
You should be prepared by knowing Hurak’s Mental Health First Aid Courses.
Enrol in our Mental Health First Aid Course today.
Are Spiders Scared of Humans?
Spiders are naturally afraid of humans and will avoid contact whenever possible. They are far more interested in staying hidden than interacting with people.
Although many people feel uneasy around spiders, it’s important to remember that spiders are much more afraid of us. The table below shows how humans and spiders perceive each other and why encounters usually trigger a quick escape rather than aggression.
Aspect | Humans | Spiders |
Size Comparison | See spiders as small, sometimes threatening creatures | See humans as huge predators |
Response to Encounter | Often feel fear, disgust, or panic | Instinctively flee or hide |
Intentions | Worry about being bitten or surprised | Want to avoid contact and stay unnoticed |
Defense Behavior | Avoid, kill, or remove spiders | Escape, freeze, or hide |
Likelihood of Attack | May attempt to remove or squash | Only bite if trapped or threatened |
Preferred Environment | Clean, bright spaces | Dark, quiet, undisturbed areas away from humans |
What Causes Arachnophobia?
Arachnophobia doesn’t develop out of nowhere. Instead, it often results from a combination of biological, psychological, and environmental factors. Understanding these causes can help you see why the fear feels so strong and why it can be hard to shake without help.
- Evolutionary Survival Instincts: From an evolutionary perspective, humans who avoided venomous creatures like spiders were more likely to survive. This ancient survival mechanism can still influence us today, even though most modern spiders are harmless.
- Negative or Traumatic Experiences: A sudden or frightening encounter—like a spider crawling across your body or appearing unexpectedly—can leave a lasting impression. Even a single incident in childhood can trigger a phobia later on.
- Observational Learning: If you saw a parent or caregiver react fearfully to spiders, you may have learned to associate spiders with danger. This is known as modeling, and it’s especially powerful in early childhood.
- Cultural and Media Influences: Spiders are often portrayed in movies, books, and folklore as dangerous, creepy, or evil. These negative images reinforce the idea that spiders are something to fear.
- Disgust Sensitivity: Some researchers suggest that people who are highly sensitive to feelings of disgust may be more likely to develop arachnophobia. The spider’s appearance, many legs, rapid movement, or unusual body shape can trigger strong aversion.
- Genetic Factors: Phobias can sometimes run in families. While this may partly be due to learned behaviors, there could also be a genetic predisposition to anxiety-related conditions, including specific phobias like arachnophobia.
Common Symptoms of Arachnophobia
People with arachnophobia experience a wide range of physical, emotional, and behavioral symptoms. These reactions can occur when seeing a spider, thinking about one, or even encountering pictures or videos. These symptoms can vary in intensity. Some people feel mild unease, while others experience severe panic attacks. If your fear is interfering with daily life, professional help is available and effective.
Physical Symptoms:
When someone with arachnophobia encounters a spider, or even just thinks about one, their body can react as if it’s in real danger. These physical responses are triggered by the body’s natural fight-or-flight mechanism and can be intense and immediate.
- Rapid heartbeat or palpitations
- Shortness of breath
- Sweating or chills
- Trembling or shaking
- Nausea, dizziness, or feeling faint
Emotional Symptoms:
Emotionally, arachnophobia can feel overwhelming. The fear often goes far beyond simple dislike and can cause powerful feelings of panic, dread, or helplessness that are difficult to control.
- Intense fear or panic
- Overwhelming sense of dread
- Feeling trapped or out of control
Cognitive Symptoms:
Arachnophobia doesn’t just affect how you feel; it also influences how you think. People with this phobia may have persistent, intrusive thoughts about spiders and overestimate the danger they pose.
- Persistent thoughts about spiders
- Believing spiders are more dangerous than they are
- Worrying excessively about encountering spiders
Behavioural Symptoms:
To avoid triggering their fear, many people with arachnophobia change their habits or routines. This can lead to avoidance behaviors that interfere with daily life and limit where they feel safe.
- Avoiding certain places (basements, attics, sheds, gardens)
- Refusing to enter rooms without checking for spiders
- Leaving the area immediately if a spider is seen
How to Get Over a Fear of Spiders?
Combining several of these strategies often leads to the best results. Be patient with yourself; progress takes time, but many people see significant improvement. This table shows a description for a better understanding of the process:
Strategy | Description |
Gradual Exposure Therapy | Slowly face your fear in controlled steps. Start by looking at pictures, then videos, and eventually observe real spiders from a safe distance. |
Cognitive Behavioural Therapy (CBT) | Work with a therapist to challenge negative thoughts about spiders and replace them with more balanced, realistic beliefs. |
Relaxation Techniques | Practice deep breathing, mindfulness, or progressive muscle relaxation to manage anxiety when you encounter or think about spiders. |
Education and Reframing | Learn factual information about spiders to counter myths and reduce exaggerated fears about their danger. |
Professional Support | Seek help from a mental health professional specialising in phobias for personalised treatment plans and guidance. |
Support Groups & Resources | Connect with others who share your fear through online communities, support groups, or educational resources for encouragement and practical advice. |
Conclusion
Arachnophobia is a common fear that can feel overwhelming, but it doesn’t have to control your life. By understanding why it happens and exploring proven treatments like exposure therapy and cognitive behavioural techniques, you can take meaningful steps toward overcoming it. If you’re struggling, don’t hesitate to reach out for professional guidance and support. With the right support and a willingness to face your fear gradually, lasting change is possible.
FAQs
What is arachnophobia?
Arachnophobia is an intense, irrational fear of spiders and other arachnids. It’s a specific phobia that can cause anxiety, panic attacks, and avoidance behaviors.
Why are people so afraid of spiders?
Fear of spiders can stem from evolutionary survival instincts, past negative experiences, cultural influences, and learned behavior. Even harmless spiders can trigger this response.
How common is arachnophobia in the UK?
Around 3–5% of people in the UK have severe arachnophobia, while up to 50% report some level of fear or discomfort around spiders.
Can arachnophobia be cured?
Yes. With treatments like exposure therapy, cognitive behavioral therapy, and relaxation techniques, many people successfully overcome or greatly reduce their fear.
What should I do if I see a spider and panic?
Take slow, deep breaths to calm your body. Focus on grounding yourself in the present moment. If possible, gently remove the spider or leave the area until you feel calmer.





