Fires are unpredictable, but your response to them doesn’t have to be. Whether you’re working in construction, retail, hospitality, or an office, understanding fire extinguishers is essential. It’s not just about reacting in emergencies; it’s about being prepared, responsible, and compliant with UK workplace safety standards.
This guide explains the various types of fire extinguishers, their relationship to fire classes, and how to use them safely, whether you’re new to the topic or a workplace supervisor managing health and safety.
What Are Fire Classes and Why Do They Matter?
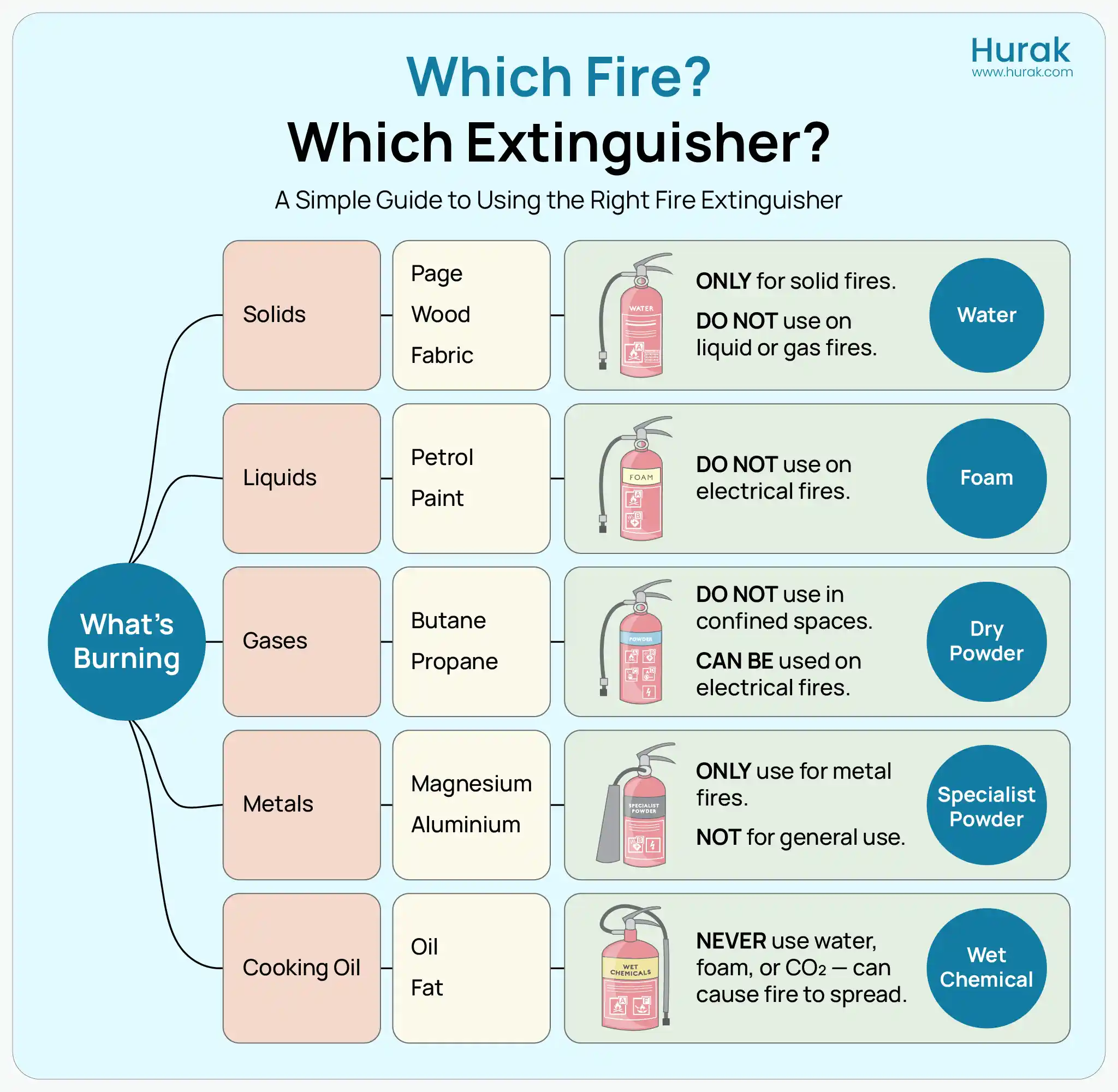
In the UK, fires are grouped into classes based on the type of material that’s burning. This classification is important because each fire type requires a different extinguishing method. Using the wrong one can be dangerous or even fatal.
- Class A: Solid combustibles like wood, paper, fabric
- Class B: Flammable liquids such as petrol, oils, and solvents
- Class C: Flammable gases like propane or butane
- Class D: Flammable metals (e.g. magnesium, aluminium)
- Class F: Cooking oils and fats (common in kitchens)
- Electrical Fires: Not a separate class, but a common and serious risk involving powered equipment
Once you understand what’s burning, you can safely match the fire to the correct type of extinguisher.
Want a deeper understanding of the dangers in the workplace? See our post on common health and safety risks on construction sites.
Types of Fire Extinguishers (and What They’re Used For)
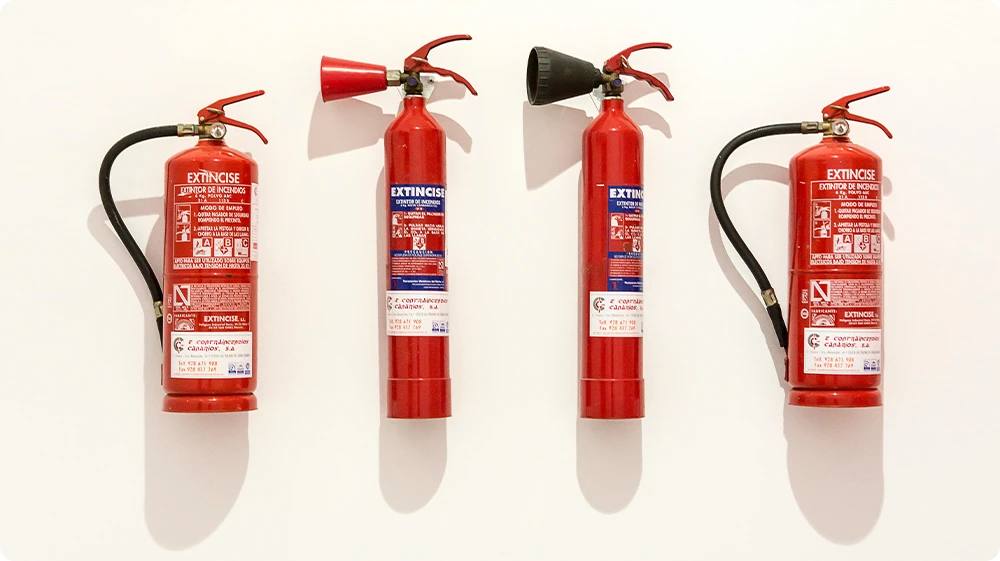
Fire extinguishers in the UK are colour-coded and designed to fight specific fire classes. Here’s a detailed look at the most common types you’ll see in the workplace:
Water Extinguisher (Red Label)
Water extinguishers are used for Class A fires, which involve materials such as wood, paper, or cloth. They work by cooling the burning material and reducing heat. However, they must never be used on electrical fires or flammable liquids, as this could spread the fire or result in electrocution.
These are commonly found in schools, offices, and public buildings where solid materials are the main fire risk.
Foam Extinguisher (Cream Label)
Foam extinguishers are suitable for Class A and B fires, meaning they can handle solids and flammable liquids. They work by forming a film over the liquid’s surface, cutting off oxygen. Foam extinguishers are versatile but still unsafe on live electrical equipment.
You’ll often see these in garages, workshops, and warehouses.
Dry Powder Extinguisher (Blue Label)
Also known as ABC extinguishers, dry powder models are suitable for Class A, B, and C fires and can also be used on electrical fires. They work by smothering the fire and interrupting the chemical reaction. However, they create a lot of residue and can make it hard to see or breathe indoors.
Dry powder extinguishers are useful for outdoor settings, petrol stations, and sites with mixed fire risks.
CO₂ Extinguisher (Black Label)
CO₂ extinguishers are ideal for electrical fires and flammable liquids. They work by displacing oxygen, effectively suffocating the fire. Since CO₂ leaves no residue, it’s ideal for offices, IT rooms, and electrical cabinets.
However, they’re ineffective on Class A fires and not suitable for outdoor use where wind can disperse the gas.
Wet Chemical Extinguisher (Yellow Label)
Designed explicitly for Class F fires, wet chemical extinguishers are essential in kitchens. They cool burning oil and chemically react to form a soapy layer that seals the surface and prevents re-ignition. While highly effective in kitchens, they should never be used on electrical fires.
This extinguisher is a must-have in catering environments, canteens, and food production units.
Curious about how these types apply in real settings? Read our guide to fire safety at your workplace.
🧯Be the Person Who Knows What to Do
Fire Marshals are essential in every workplace. Get trained to lead evacuations, use extinguishers safely, and prevent fire risks.
Explore the Fire Marshal Online Course
Why Using the Correct Extinguisher Is Critical
Using the wrong extinguisher can have serious consequences. For instance, spraying water on burning oil can cause the flames to spread violently. Similarly, using foam or water on an electrical fire could lead to electrocution.
Employers and designated fire wardens must ensure that the correct extinguishers are not only present but also clearly labelled, accessible, and maintained. As part of their training, they must understand how to assess which extinguisher is appropriate based on the fire class.
If you’re assigned fire safety responsibilities at work, it’s worth knowing that Fire Marshal training prepares you to take charge in emergencies, from extinguisher use to evacuation leadership.
Legal Responsibilities Under UK Law
According to the Regulatory Reform (Fire Safety) Order 2005, all workplaces in the UK are required to:
- Conduct regular fire risk assessments
- Install appropriate fire extinguishers based on identified risks
- Ensure that extinguishers are regularly serviced
- Train staff in fire awareness and extinguisher use
- Assign responsible persons for managing fire safety
These duties apply to all employers, building owners, and anyone in control of premises. Non-compliance can lead to enforcement notices, fines, or prosecution, especially if someone is harmed due to a lack of preparation.
If you’re unsure how roles and responsibilities are structured within an organisation, our article on the key responsibilities of a health and safety officer offers practical insights.
Why Training Makes the Difference
Even when the right extinguishers are in place, they’re only effective if people know how to use them. Training helps employees understand the types of fires they may face and equips them with the confidence to act safely.
If you’re just starting your health and safety journey or looking to refresh your knowledge, the Level 2 Health and Safety in the Workplace course is a great foundation. It teaches you how to identify risks, handle equipment such as extinguishers, and understand the laws that govern workplace safety.
For those in catering, retail, or hospitality roles where fire hazards are specific to the environment, such tailored training helps build long-term confidence and prevent incidents before they happen.
For further risk reduction strategies, read about how to avoid manual handling risks and the differences between risk control and hazard control, key topics in creating a safer environment.
📚Take Your Fire Safety Skills to a Professional Level
A respected qualification for those managing fire risk or aiming for specialist roles.
Discover the NEBOSH Fire Safety Certificate
Final Thoughts
Whether you’re a site supervisor, office worker, or someone responsible for safety, understanding the types of fire extinguishers is a basic yet powerful skill. It can help protect not just your workplace, but your colleagues and your future.
When matched with proper training and a commitment to compliance, even the most basic knowledge, like recognising extinguisher colours or fire classes, can save lives.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different fire extinguisher colours and what do they mean?
In the UK, fire extinguisher colours help identify their contents and appropriate use. A red label indicates a water extinguisher, suitable for solid combustibles like paper and wood. A cream label marks a foam extinguisher, used on flammable liquids and solids. A blue label represents a dry powder extinguisher, which is versatile across multiple fire classes. A black label is used for CO₂ extinguishers, ideal for electrical fires. Finally, a yellow label is for wet chemical extinguishers, designed specifically for cooking oil fires (Class F). These fire extinguisher colours make it easier to act quickly and correctly during a fire emergency.
What extinguisher should be used for electrical fires?
For an electrical fire, the safest extinguishers to use are CO₂ extinguishers (black label) and dry powder extinguishers (blue label). These types are non-conductive and won’t cause electrocution, unlike water or foam. CO₂ is often preferred in offices and server rooms because it leaves no residue, while dry powder is more suitable in industrial or outdoor areas where electrical and flammable risks coexist. If you’re unsure, always look for extinguishers that explicitly state they are safe on Class E or electrical fires.
What is a water extinguisher used for?
A water extinguisher is primarily used for Class A fires, which involve solid materials like paper, wood, and textiles. They work by cooling the flames and lowering the temperature below the ignition point. However, they should never be used on flammable liquids or electrical fires, as this can spread the fire or create electrocution hazards. You’ll usually find water extinguishers in schools, office buildings, and public spaces with low electrical risk. Understanding the purpose of a water extinguisher helps prevent its misuse in hazardous situations.
What are the 4 main types of fire extinguishers?
The four main fire extinguisher types commonly used in workplaces are water (red), foam (cream), dry powder (blue), and CO₂ (black). Each is suited for different fire classes:
- Water: For solid materials (Class A)
- Foam: For solids and flammable liquids (Class A & B)
- Dry Powder: For solids, flammable liquids, gases, and electrical equipment (A, B, C & electrical)
- CO₂: Primarily for electrical fires and flammable liquids (electrical & B)
Wet chemical extinguishers (yellow label) are also widely used in kitchens, particularly in the hospitality sector, to handle Class F fires involving cooking oils.
Which extinguisher should be used on flammable liquids?
Fires involving flammable liquids like petrol or solvents are classified as Class B fires. The best extinguishers for these are foam extinguishers (cream label) and dry powder extinguishers (blue label). CO₂ extinguishers are also effective, particularly in indoor spaces where clean use is important. Never use water extinguishers on flammable liquids; it will likely spread the fire. Knowing the right fire extinguisher for flammable liquids can prevent disasters in fuel-handling or chemical workspaces.
What are the different classes of fire in the UK?
In the UK, fires are categorised into six main classes of fire:
- Class A – solids like wood and paper
- Class B – flammable liquids such as oils, fuels, or alcohols
- Class C – flammable gases like butane or propane
- Class D – combustible metals such as magnesium or lithium
- Class F – cooking oils and fats
- Electrical fires – involving powered appliances (not a formal class but treated uniquely)
Each fire class demands a specific extinguisher, making it crucial to understand this system for safe fire management.
What type of extinguisher should be used on different materials?
Different materials ignite differently, and not all extinguishers can be used safely across them. Solid materials, such as paper and wood, require water or foam extinguishers. Flammable liquids are best handled with foam, CO₂, or dry powder. For electrical equipment, CO₂ or dry powder is the safest option. Cooking oil fires need wet chemical extinguishers, and metal fires require specialist dry powder types (not to be confused with standard ABC powder). Understanding the kind of extinguisher suitable for a particular material reduces the risk of igniting the fire.
What is the cream fire extinguisher used for?
The cream fire extinguisher is a foam extinguisher. It’s used on Class A and B fires, which involve solids (such as paper and textiles) and flammable liquids (like petrol or paint). It works by creating a cooling foam barrier that suffocates the fire and prevents re-ignition. However, cream extinguishers should never be used on electrical fires, as foam conducts electricity. These are common in industrial and commercial environments where both solid and liquid fire risks are present.
Explore Related Courses
Looking to boost your confidence in handling fire safety and workplace risks? These trusted courses can help:
- Level 2 Health and Safety in the Workplace – Covers core safety principles, including fire prevention and hazard awareness.
- Fire Marshal / Fire Warden Online – Learn how to respond to workplace fires and lead safe evacuations.
- SSSTS (Site Supervisor Safety Training Scheme) – Ideal for those supervising high-risk environments like construction sites.
- SMSTS (Site Management Safety Training Scheme) – A comprehensive course for managers overseeing fire and site safety.





