Millions of individuals worldwide are impacted by epilepsy, including those who support or care for those with the disorder. It is a typical neurological illness that can afflict anyone, regardless of age, sex, or race, and frequently results in seizures.
The definition of epilepsy, key distinctions between it and seizures, indications and symptoms of a seizure, ways to support someone with epilepsy, and what to do in the case of a seizure are all covered in this article.
What is epilepsy?
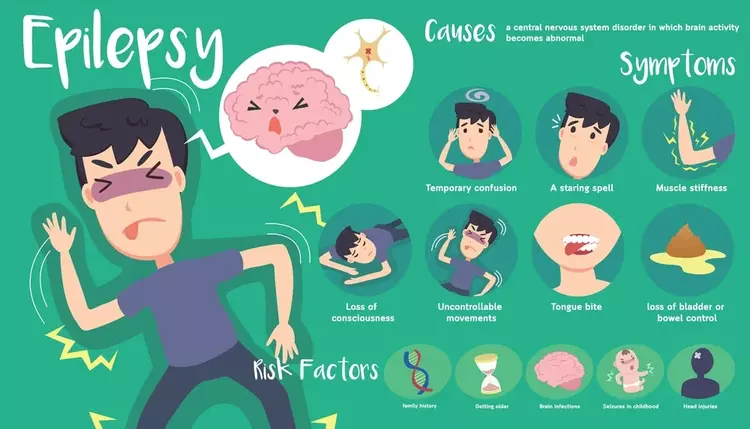
A frequent disorder that affects the brain and can result in seizures is epilepsy. Brain electrical activity surges, known as seizures, can cause symptoms like losing consciousness, trembling, or falling.
Epilepsy typically begins in childhood or after age 60 and lasts a lifetime. Epilepsy symptoms can sometimes be controlled with medicine, and the illness occasionally gets better with time. However, epilepsy is a chronic disorder for many people.
Each individual’s case of epilepsy has a unique set of causes, which are numerous and varied. A severe head injury, a stroke, or an infection of the brain are a few typical causes of brain damage.
There are various varieties of epilepsy as well as various causes. Four different forms of epilepsy have been identified by the International League Against Epilepsy (ILAE).
- Focal epilepsy – seizures that start on just one side of the brain.
- Generalised epilepsy – starts on both sides of the brain.
- Combined generalised and focused epilepsy – are a part of combined general and focal epilepsy.
- Unknown – Sometimes, it is difficult to pinpoint the origin of these kinds of seizures.
What are the differences between epilepsy and seizures?
An electrical surge in the brain, known as a seizure, can result in aberrant muscle tone, movements, behaviours, perceptions, and levels of consciousness. Depending on whatever portion of the brain is affected, seizures have a distinct impact on various people. People frequently fall to the ground during generalised seizures, for instance.
Numerous factors, including drug usage, high blood sugar, and fever, can cause seizures. It is typically accepted that someone has epilepsy if they experience two or more seizures separated by at least 24 hours.
It is significant to remember that seizures can occur in people who do not have epilepsy. Seizures are necessary for epilepsy, even if they don’t have overt consequences. Seizures, as was previously established, are not always brought on by epilepsy and can be brought on by various factors.
Making the distinction between seizure triggers and epilepsy causes is crucial. For instance, a person with epilepsy who is sleep deprived may experience a seizure. The seizure is brought on by insufficient sleep, but brain damage may be the underlying factor in their epilepsy. In this case, the seizure rather than the lack of sleep is what has triggered their epilepsy.
Among the causes of epilepsy are:
- A brain infection.
- A lack of oxygen during birth.
- Genetics.
- Alzheimer’s disease.
- A brain or head injury.
- A brain tumour.
- Drug or alcohol misuse.
- A stroke.
Seizure-inducing factors include:
- Missing medication.
- Changes in hormones.
- A fever is especially common in children.
- Stress.
- A lack of sleep.
- Alcohol and recreational drugs.
- Skipping or missing meals.
- Over excitement.
- Flashing and flickering lights.
What are the symptoms and signs of epileptic seizures?
Depending on the type of seizure a person is experiencing, their signs and symptoms will change. Not all seizures are accompanied by strange shaking or body movements, and some last only a few seconds.
The following are some symptoms and warning indicators that someone may be suffering an epileptic seizure:
- Rapid blinking.
- Breathing problems.
- Appear confused or in a daze.
- Unconsciousness.
- Losing muscle tone.
- Changes in hearing, vision, taste, smell and feel.
- Difficulty talking.
- An increased heart rate.
- Lip-smacking, chewing motions, or rubbing hands and fingers.
- Uncontrollable body movements, shaking or jerking.
People must be aware of a seizure’s warning signs and symptoms to recognise it quickly and render aid if necessary.
Particularly if they persist for more than five minutes or the victim stops breathing, seizures can be exceedingly dangerous. Knowing how to assist someone with epilepsy during a seizure is vital since seizures can cause other injuries, such as bruises, scrapes, and head trauma.

Our First Aid at Work training course describes the various reactions to various kinds of seizures, how to spot an emergency, and how to assist a person after a seizure.
Get Trained in All First-Aid Skills
First Aid Courses
Book NowRated Excellent
on major review sites

How to help someone with epilepsy?
Each person with epilepsy is different; thus, the kind of support they need will differ. You can only provide someone with the most suitable and helpful assistance if you comprehend how their disease affects them.
How to respond to seizures?
Respond as follows if someone is having a seizure:
Do:
- Remove any dangerous things from the area.
- Remain composed, reassuring, and by their side until the seizure is done.
- After the seizure, check in with them to see if they’re alright and give them a seat.
Don’t:
- Do not grab them, restrain them, or make any sudden motions.
- Presume that they are aware of what is taking place.
- Try to entice them over or provide them with food or beverages.
‘Call 112 or 999 if:
- A person has a series of seizures without gaining awareness between them.
- It is their first seizure.
- More than five minutes pass as the seizure continues.
- The individual is hurt, or you believe they require medical attention.
As previously said, the sort of seizure the person is experiencing will determine how you should react. Take a look at one of our first aid training courses if you want to understand how to handle various seizure types and how to spot an emergency.
Some people will recover from a seizure immediately, while others may need a few minutes or even hours. People may experience confusion and fatigue during the postictal state, which is the period following a seizure. The best method to provide support is to be there for the person and stick with them till they recover.
Learning about it and spreading as much information as possible to increase awareness are two of the most significant things you can do for a friend with epilepsy. The complexity of epilepsy is more than most people realise, and any knowledge gained is beneficial to all those who are affected.