Food preservation keeps food safe to eat for a longer time, by stopping bacteria and spores from growing.
What is Food Preservation?
Food preservation primarily provides protection from germs. It is the process that extends the shelf life of food by protecting it from microbial contamination.
The time duration that food stays good to eat is called its “shelf life.” Perishable food is used sooner because its shelf life runs out quickly. Non-perishable food has a long shelf life and can be stored for later use.
How Do You Preserve Food
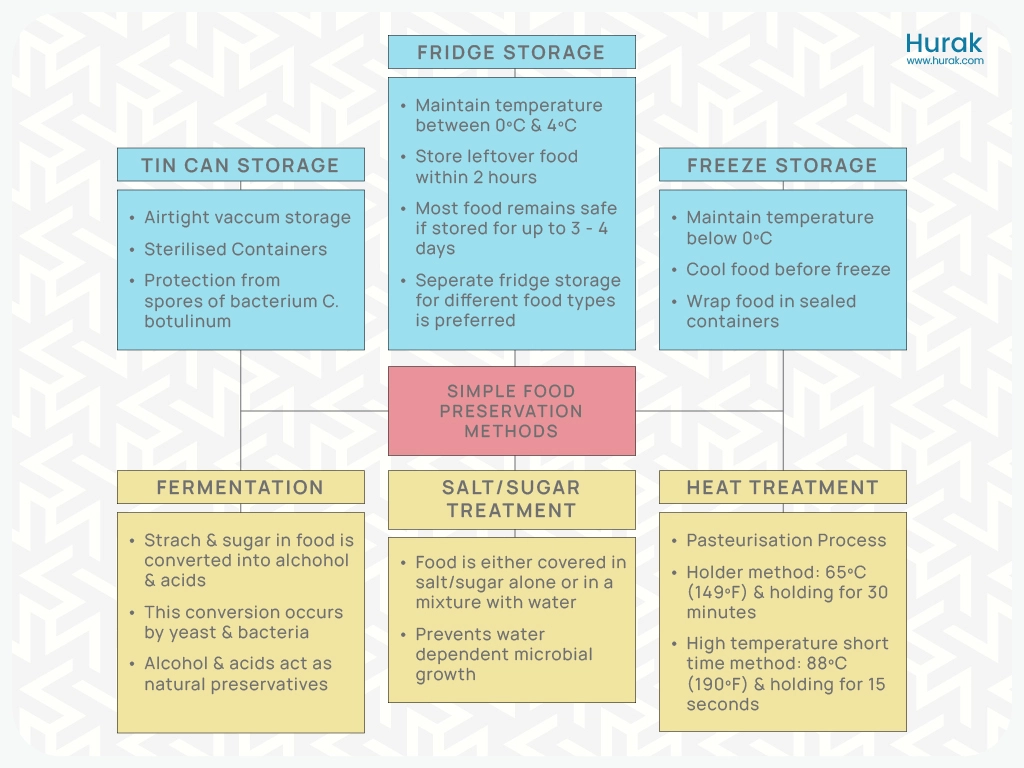
There are different ways to preserve food. Here are some common ones:
- Putting food in the fridge
- Storing food in the freezer
- Putting food in cans made of aluminium or tin
- Adding salt or sugar to food
- Letting food ferment
- Treating food with heat
These methods help stop bacteria from growing and spoiling the food. They either take out water, keep it cold, seal it in a vacuum, or heat it to make it last longer
Putting Food in the Fridge
- Storing food at a low temperature between 0 and 4 degrees celsius, slows down bacterial spread and keeps food fresh.
- Refrigerated food remains out of the “Danger Zone” Temperature at 40 °F and 140 °F (8 °C and 60 °C). At the danger zone temperature, the growth of bacteria is twice as rapid.
- Fridge storage of food at below 5 °C for up to 3 to 4 days in most cases is preferred to prevent spoilage.
- Food leftovers should be stored within 2 hours to prevent prolonged exposure to room temperature.
- It is important to arrange food correctly stored in separate compartments or sealed containers, to prevent cross-contamination.
- Ideally, food items stored first must also be consumed first. The First-In First-Out (FIFO) rule confirms that food is used before it expires, reducing food waste.
Storing Food in the Freezer
- Freezer temperature usually ranges between -18°C and 0°C.
- Freezing food slows down the growth of bacteria and enzymatic activity, preserving freshness and nutrients.
- Food stored in a freezer can remain preserved for up to several months.
- It is important to cool food before freezing it.
- Freezing causes water molecules to form crystals of ice.
- The method reduces the amount of free water needed for microbial and enzymatic reactions.
- Always maintain the freezer to the lowest temperature for proper crystal formation.
- Freezing does not aim to sterilise food, it keeps the quality of food intact.

Putting Food in Cans Made of Aluminium or Tin
- Storing food in tin containers protects food from bacterial toxins.
- The container is sterilised using intense heat.
- High temperatures in a pressure canner destroy harmful microorganisms like Clostridium botulinum spores.
- The required temperature for destroying these spores is 240°F (116°C).
- During canning, the heat treatment kills vegetative bacteria, yeasts and moulds.
- The high temperature also interferes with the process of microbial cell wall synthesis, protein production and metabolism.
- Food is stored in a can under airtight conditions. The can is further heated to destroy microorganisms.
- High-acid foods (low PH) such as fruits and pickles undergo low heat intensities during canning.
- Foods low in acidity require high temperatures for canning. Examples include meat and soups.
Adding Salt or Sugar to Food
- Sugar and salt act as natural preservatives in food by reducing water activity and slowing microbial growth.
- Wet or dry sugar/salt treatment can help preserve food through desiccation or extreme dying.
- Drying occurs by osmosis when water moves from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration.
- Water in food responsible for bacterial growth moves out into the salty environment of low water concentration.
- Sugar and salt-driven osmotic pressure leads to unfavourable conditions for microorganisms in water-starved environments.
Letting Food Ferment
- Fermentation is the oldest method of food preservation that preserves the freshness of food through bacterial activity.
- Fermentation causes acidification that inhibits the growth of microorganisms such as yeast, bacteria and moulds.
- Microorganisms produce alcohols and organic acids from sugars. As a result, unfavourable environmental conditions are created for bacterial spread. The quality of food is preserved, and the shelf-life is prolonged.
- Some microorganisms produce preservative compounds that help maintain the safety and quality of fermented foods.
- Usually, there is no need to add chemicals or artificial additives in fermented foods.
- Fermentation occurs in an anaerobic environment that slows the growth of aerobic bacteria.
- The process of fermentation prevents unwanted oxidation of food.
- Fermentation produces vitamins, enzymes, and bioactive compounds to maintain the nutritional value and health benefits of fermented foods.
Treating Food with Heat
- Pasteurisation reduces microbiological presence in solid and liquid foods by using high intensities of heat.
- The process does not kill microbial growth at 100%.
- Pasteurised foods have a limited shelf life and require refrigeration due to the presence of surviving microorganisms.
- The main difference between the process of sterilisation in canning and pasteurisation is that sterilisation completely destroys microorganisms and spores. On the other hand, pasteurisation reduces microbial load with the presence of some surviving microorganisms. It does not change the nutritional value and taste of food.
- Pasteurisation ‘Holder Method’ Conditions: 149°F (65°C) for 30 minutes
- Pasteurisation ‘High Temperature/Short Time (HTST)’ Conditions: 190°F (88°C) for 15 seconds
Which Food Preservation Method is the Best?
The most suitable preservation method depends on factors such as the type of food, and the desired shelf life. For example, canning is suitable for preserving fruits and vegetables. Freezing is used for preserving meats and seafood.
Bacterial Spores in Food
The shape of bacterial spores is oval or sphere-like. They are small dormant forms of bacteria that are highly resistant to heat, desiccation, and chemical agents. They survive high temperatures, up to 150°C (302°F). Spores can multiply and lead to food spoilage and potential health risks.
Importance of Food Preservation in Food Safety
- Prevents the growth of harmful microorganisms that cause foodborne illnesses
- Prolongs the shelf life of perishable food items
- Reduces the risk of consuming contaminated food
- Protects consumers from foodborne pathogens such as Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria
- Minimises food waste by allowing extra food to be stored
- Saves money and reduces the environmental impact of food production and distribution.
Get Online Food Safety Courses
Food Hygiene And Safety
Check the CourseRated Excellent
on major review sites

Disadvantages of Food Preservation Methods
Food preservation methods offer several benefits, but they also have some drawbacks:
- Canning and drying can lead to a loss of vitamins and minerals in food.
- Some preserved foods have reduced palatability due to changes in texture and flavour.
- Packaging materials used in food preservation methods, such as cans and plastic containers, can have negative environmental consequences.
FAQs
What is the difference between pasteurisation and sterilisation?
Sterilisation completely eliminates microorganisms and spores. On the other hand, pasteurisation reduces microbial load with the presence of some surviving bacteria.
What temperature can spores survive?
The correct temperature for storing food in a fridge is at below 5 °C for up to 3 to 4 days.
What is the correct temperature for storing food in a fridge?
Fridge storage of food at below 5 °C for up to 3 to 4 days in most cases is preferred to prevent spoilage.
What is food preservation?
Food preservation is the process that extends the shelf life of food items by protecting them from microbial contamination.
What are the common methods of food preservation?
Common methods for preserving food are fridge/freezer storage, tin can storage, salt or sugar treatment, fermentation and heat treatment.
Conclusion
Food preservation protects food from microbial contamination. It maintains food safety, quality, and nutritional value. Methods of food preservation include fridge and freezer storage, tin can storage, salt or sugar treatment, fermentation, and heat treatment. They inhibit bacterial growth and prolong the freshness of food. Each preservation method is best suited based on the type of food and desired shelf life. Despite some drawbacks, food preservation methods contribute greatly to food safety.




